Glossary
Easy-to-understand definitions for common cybersecurity terms and topics.
Hello!
You’re about to visit our web page in English
Would you like to continue?
If this is not what you’re looking for,
There are different types of malware and varying degrees of danger. However, as a general rule, the objectives of malware are usually one of the following:
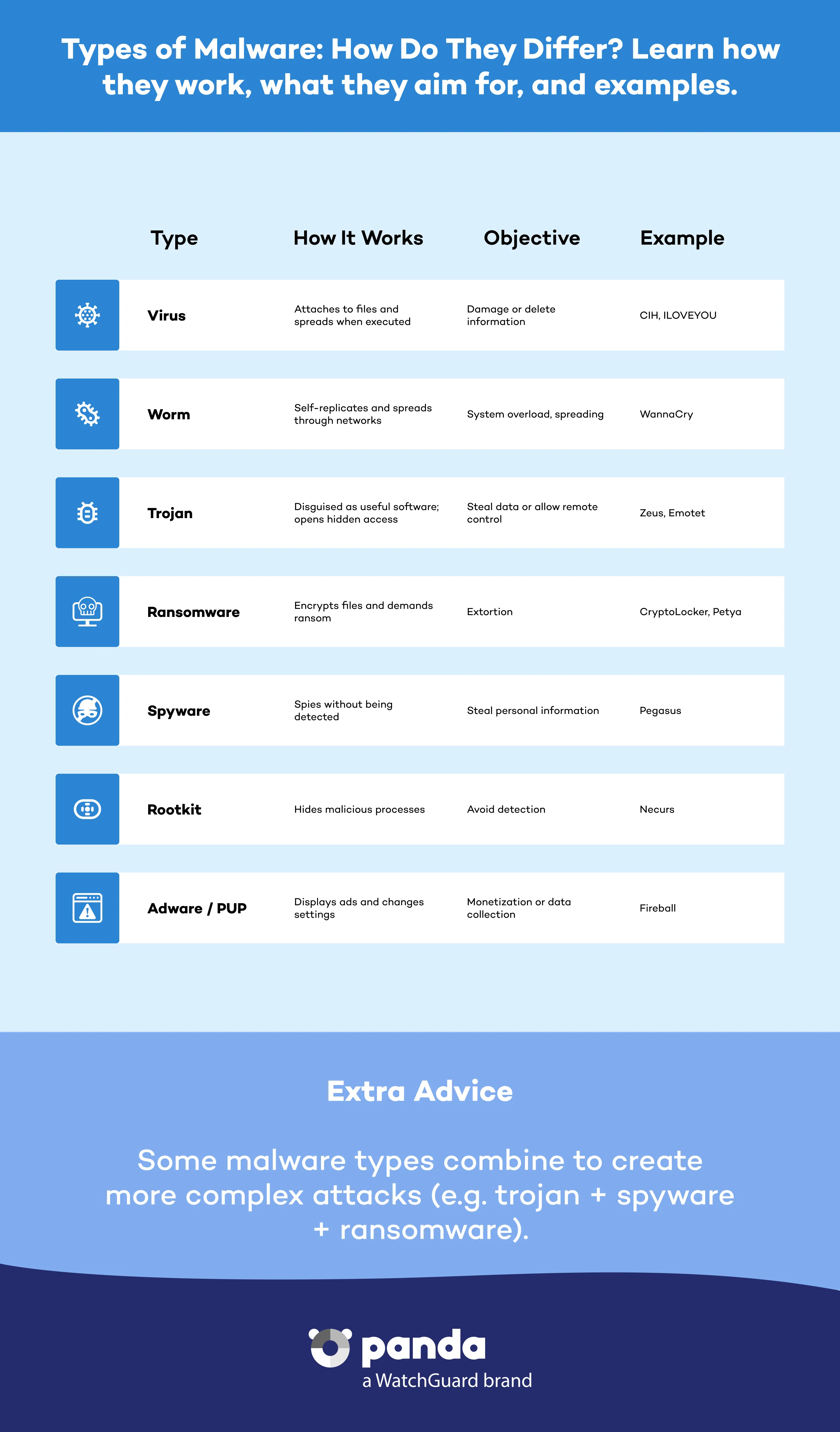
A virus is a program that enters computers and IT systems in a number of ways, causing effects that range from simply annoying to highly destructive and irreparable.
A worm is a program similar to a virus which, unlike a virus, only makes copies of itself or parts of it.
Strictly speaking, a Trojan is not a virus, even though it is often thought of as such. It is really a program that reaches computers disguised as harmless software to install itself on computers and carry out actions that compromise user confidentiality. The name comes from the mythological story of the Trojan horse.
A rootkit is a program designed to hide elements such as processes, files, or Windows Registry entries, including its own. Although not malicious in itself, cybercriminals use it to conceal activities and tools on compromised systems. Some types of malware incorporate rootkits in order to remain undetectable and persist on an infected system.
Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents a user from accessing their system until they pay a ransom. Well-known variants of ransomware include:
WannaCry was notable for exploiting a vulnerability in the Windows operating system, allowing it to spread massively, affecting individual users and large organizations alike.
CryptoLocker encrypts files on a user's system and demands payment in Bitcoin in return for the decryption key.
Petya encrypts the master boot record (MBR) of infected systems, preventing access to the operating system by completely blocking access to the hard drive. Petya and its variants, such as NotPetya, have been used in massive attacks affecting both businesses and individual users.
PUPs are applications which, although not considered malware, are installed without the user's explicit consent or through deception. They can affect system performance or modify settings without authorization.
Adware is software designed to display intrusive advertisements on a user's system, often without their consent. It can collect data about a user’s Internet habits to personalize ads or redirect victims to suspicious websites.
Spyware is a type of malicious software that collects users’ information without their knowledge, such as login credentials, browsing history, or personal data, and sends it to third parties for advertising or fraudulent purposes.
Scareware is a program that generates fake security alerts to scare users into believing their system has been infected. It often encourages users to purchase fraudulent software or download malicious programs.
Rogueware is a variant of scareware which is disguised as legitimate security software, such as a fake antivirus, to trick users into paying for an ineffective or even potentially dangerous security solution.
Intrusion and remote control techniques are used by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to computer systems and control them without the user's knowledge. These tools allow malicious actions, such as stealing information, manipulating a system, or installing other types of malware.
A backdoor is a type of malicious software or code that allows remote access to a system without being detected by security solutions. It can be used by attackers to control infected devices, steal information, or run commands in the background without the user's consent.
A dialer is a malicious program that connects to premium-rate telephone numbers without the user's consent. Although it was more common in the era of modem connections, it remains a threat today on some vulnerable devices, generating unexpected charges on telephone bills.
A keylogger is malicious software or hardware designed to record a user's keystrokes, in order to steal login credentials, banking data, and other sensitive information that can later be used in fraud or identity theft attacks. These programs often operate silently to avoid detection.
Malware spreads in various different ways in order to infect as many devices as possible. One of the most common methods is distribution through P2P (peer-to-peer) networks, where malicious files are disguised as legitimate content to deceive users.
File-sharing platforms such as BitTorrent are used by cybercriminals to spread malware disguised as legitimate software, games, movies, and other files. By downloading files from untrusted sources, users run the risk of infecting their devices with viruses, Trojans, or ransomware. It is essential to verify the source of files before downloading them to avoid potential threats.

The best defense against malware is prevention and the use of appropriate security tools. Follow these recommendations and strengthen your protection with Panda Dome, an advanced cybersecurity solution providing multiple layers of defense:
Think Before You Click Don’t click suspicious links or links sent from unknown sources. Panda Dome includes anti-malware and anti-phishing protection, blocking malicious websites before they can infect your device.
Who Is Offering the App? Download software only from official sources. Panda Dome has an app and file scanner that detects and blocks malware before it is even installed.
Don’t Leave It until Tomorrow! Keep operating systems and programs up to date to fix vulnerabilities. Panda Dome provides vulnerability scanning tools, helping you identify weak points on your devices.
Use Strong Passwords Protect your identity with strong, unique login credentials. Panda Dome Password Managermakes password management easy and prevents passwords from being stolen by keyloggers or brute-force attacks.
Use an Advanced Cybersecurity Platform Panda Panda Security provides anti-malware in real time, firewall, protection against ransomware and VPN, ensuring comprehensive defense against any digital threats.
Discover the Panda Dome plan that best fits your needs
You can take a look to every single product page (Panda Dome Essential, Panda Dome Advanced, Panda Dome Complete and Panda Dome Premium) or compare all our plans to take a decision.
Digital security is everyone's responsibility. With the right information and tools, you can reduce risks and use the Internet with peace of mind. Explore our guides and protect your online privacy.
Glossary
Easy-to-understand definitions for common cybersecurity terms and topics.
Panda Security Blog
Discover expert advice, detailed tips, and the latest cybersecurity news.

Panda Security, a WatchGuard Technologies brand, offers the most advanced protection for your family and business. Its Panda Dome range provides maximum security against viruses, ransomware and computer espionage, and is compatible with Windows, Mac, Android and iOS.