Many people think incognito or private mode makes their browsing completely invisible, but that’s not the full story. While your browser won’t save the sites you visit, your internet provider, employer or even certain apps might still track what you do.
If staying anonymous on the internet matters to you, it’s important to know how to see incognito history and delete it. Learn how to do it on various devices and what you can do to keep your browsing truly private.
What Is Incognito Mode and How Does It Work?
Incognito mode, also called private browsing, is a setting in browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari and Edge that lets you surf the web without saving your activity on your device.
When you open a private window, your browser won’t store your browsing history, search entries, cookies or form data. Once you close that window, it’s like those visits never happened — at least on your computer.
For example, if you use incognito mode to look up birthday gift ideas on a shared laptop, those searches won’t appear in your history or autofill suggestions.
What Incognito Mode Does Not Do
Incognito mode is not a privacy shield. It doesn’t hide what you do online from your internet service provider (ISP), your employer or school network or the websites you visit. These groups can still track the sites you access, the time spent and sometimes even your location or device type.
Think of incognito mode as a “don’t save this locally” button, not a full disguise. It mainly keeps your browsing private from others who use your device, not from the internet itself.
Why People Want to See Incognito History
There are several reasons why someone might want to view incognito history. While private browsing hides activity locally, it can still leave traces that are useful (or concerning) in certain situations.
Here are some of the most common reasons:
- Monitor children’s online activity: Parents often check incognito history to ensure their kids aren’t visiting unsafe or inappropriate websites. Even if the browser doesn’t save history, network logs or router records can reveal what sites were accessed.
- Recover lost or closed tabs: Sometimes you close an incognito window too soon and lose important information — like a booking confirmation or an article you were reading. Checking incognito traces can help you recover what you need.
- Audit browser behavior for security testing: Cybersecurity professionals and IT admins sometimes analyze incognito sessions to test how private browsing handles cookies, cached files or IP address exposure. It’s part of understanding how well privacy tools actually work.
- Detect unauthorized device activity: If you suspect someone used your device without permission, viewing incognito traces can confirm whether any private sessions occurred and what kind of sites were accessed.
- Review network-level activity: In workplaces or schools, admins may review browsing logs to ensure compliance with policies. Even when incognito mode is used, the IP address linked to a device still appears in network records.
- Verify online anonymity: Some users simply want to check if their browsing truly stays private. By viewing what’s still visible, such as DNS requests or IP data, they can understand where incognito mode’s limits begin.
How to See Incognito History on Any Device
Even though browsers don’t store incognito history locally, there are still a few ways to view traces of private browsing activity. Depending on your device and network setup, you can check DNS records, router logs or use certain apps and tools to see what was accessed in private mode.
On Mac
Mac computers don’t save incognito history directly, but you can check your DNS cache to see recently visited websites. Here’s how:
- Open Applications > Utilities > Console.
- Enter any:mdnsresponder in search.
- Click Start.
- Go back to Utilities > Terminal.
- Enter: sudo killall -INFO mDNSResponder and press Enter.
- Enter your password when asked.
- Re-open Console, and you should see your incognito history.
This works best if you haven’t restarted your Mac or cleared your DNS cache since the browsing session.
On Windows

Windows doesn’t keep incognito records in your browser, but your system’s DNS cache often holds domain information. Follow these steps to check incognito history on Windows:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type cmd and press Enter to open Command Prompt.
- Type ipconfig /displaydns and hit Enter.
- Scroll through the list of domains visited. Sites accessed in incognito mode may still appear here.
- To clear the list afterward, type ipconfig /flushdns.
On Android or iOS

Here’s how to see incognito history on a phone (Android or iOS):
- Open your device’s Settings and go to Wi-Fi or Network.
- Tap your connected network and note the router’s IP address.
- Open that IP address in your browser to access router settings (usually something like 192.168.1.1).
- Log in with your credentials.
- Look for a Logs, History or Connected Devices section.
- Review recent browsing activity — this may include sites visited from incognito tabs.
Using Chrome Extension
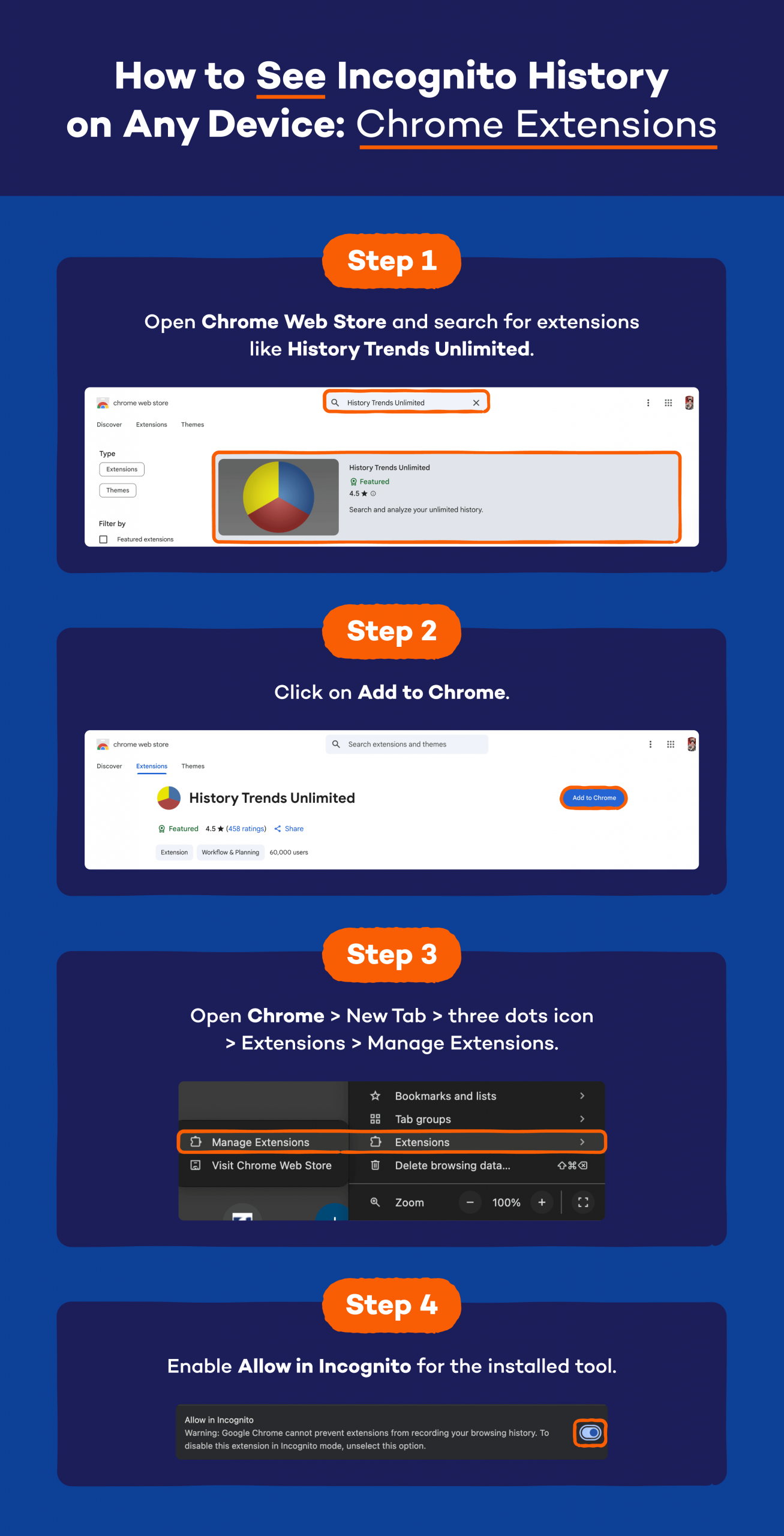
- Open Chrome Web Store and search for extensions like History Trends Unlimited.
- Click on Add to Chrome.
- Open Chrome > New Tab > three dots icon > Extensions > Manage Extensions.
- Enable Allow in Incognito for the installed tool.
- The extension will now log browsing activity, including from private windows.
- You can view recorded activity in the extension dashboard.
Only use reputable extensions and review permissions carefully.
Checking Router or Network Logs
Your router records all domains accessed through your network — incognito or not. To check incognito history using your router:
- Find your router’s IP address (usually printed on the device or shown in your Wi-Fi settings).
- Enter it in your browser to open the router’s admin panel.
- Log in with your admin username and password.
- Go to Logs or History under the Advanced or Security section.
- You’ll see a list of websites visited by devices on your network, along with time stamps and IP addresses.
Using Parental Control Apps
Parental control or monitoring apps can track browsing activity, even when using private mode. Here’s how to check incognito history using parental control apps:
- Choose a trusted app like Panda Dome Family.
- Install the app on the target device and follow the setup instructions.
- Enable web activity tracking or content filtering.
- Open the app’s dashboard to view visited sites and usage reports.
- Use this data to monitor activity, manage screen time or block harmful content.
How to Delete a Device’s Incognito History
Even though incognito mode doesn’t save your browsing history, some traces — like DNS records, cached data or network logs — can still remain. Deleting these helps you fully clear any sign of private browsing from your device. Here’s how to do it on different platforms and devices.
Mac
On a Mac, incognito traces can linger in the DNS cache or temporary files. Here’s how to wipe them completely:
- Open Terminal from your Applications > Utilities folder.
- Type the command: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder and press Enter.
- Enter your password if prompted.
- This command clears your DNS cache, removing stored site lookups.
Windows

- Press Windows + R and type cmd, then hit Enter.
- In the Command Prompt, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter to clear the DNS cache.
- Next, open File Explorer and type %temp% in the address bar.
- Select all files (Ctrl + A) and delete them.
- Empty your Recycle Bin to remove those files permanently.
This removes cached site lookups and temporary data that might reveal browsing activity.
Android
Android browsers don’t save incognito sessions, but deleting DNS cache and app data ensures no trace is left behind.
- Open Settings > Apps > Chrome (or your preferred browser).
- Tap Storage & cache.
- Select Clear Cache and then Clear Storage (if you want a complete reset).
- To clear DNS cache, open Chrome and go to the address bar. Type chrome://net-internals/#dns.
- Tap Clear host cache.
This clears cached records that could contain indirect traces of incognito sessions.
iPhone
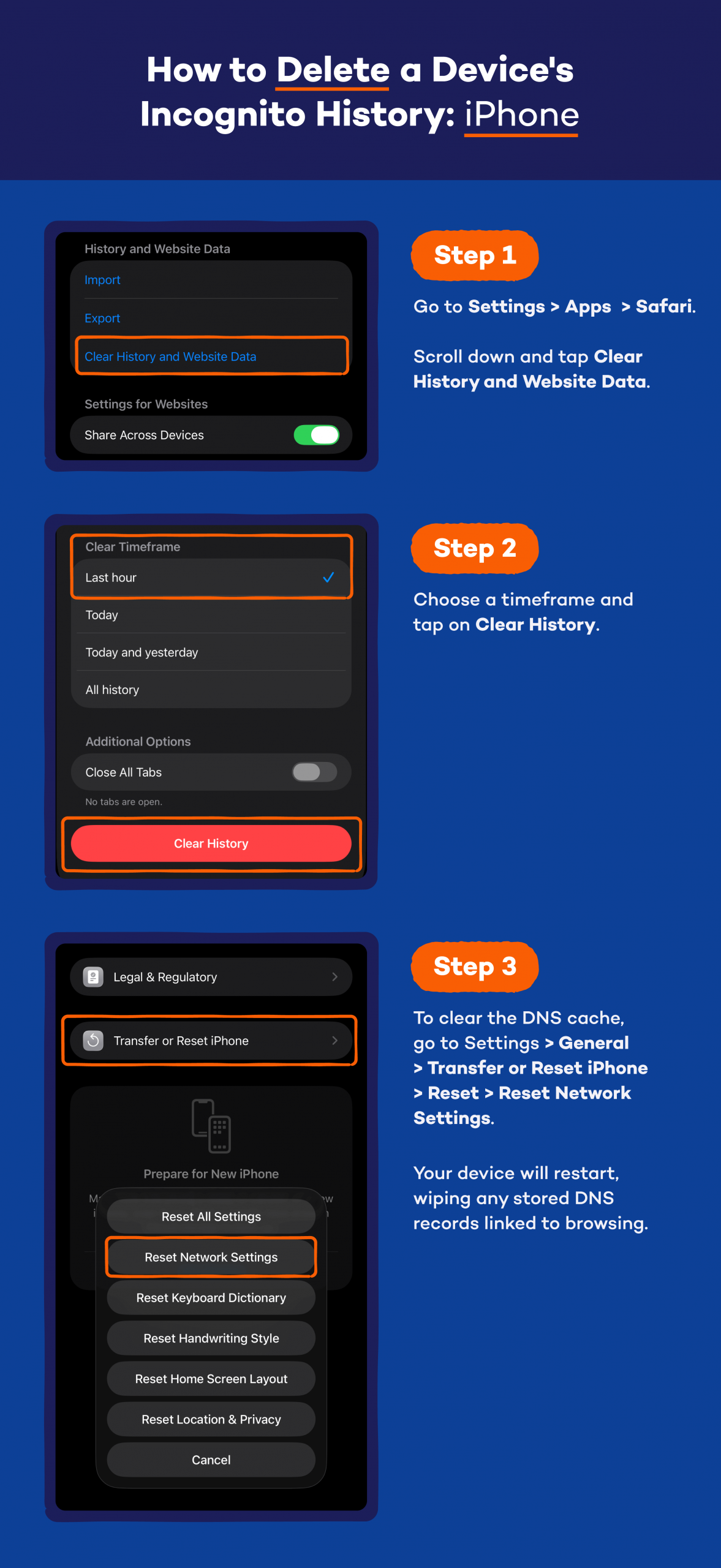
- Go to Settings > Apps > Safari.
- Scroll down and tap Clear History and Website Data.
- Choose a timeframe and tap on Clear History.
- To clear the DNS cache, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset > Reset Network Settings.
- Your device will restart, wiping any stored DNS records linked to browsing.
This process resets Safari data and clears network history to maintain full privacy.
How to Strengthen Your Online Privacy
Incognito mode is useful for keeping your local browsing history private, but it doesn’t offer complete online privacy. To truly protect your data and identity, you need extra layers of protection that hide your online activity from networks, websites and trackers. Here are a few ways to stay more secure and anonymous online.
Use a Trusted VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and hides your IP address, making it much harder for anyone — like your ISP, public Wi-Fi networks or advertisers — to track what you do online. When you use a VPN, all your data travels through a secure tunnel before reaching the internet, keeping your browsing history private even outside incognito mode.
A reliable VPN also helps protect you from data theft on unsecured networks, like airport or cafe Wi-Fi. This extra layer of encryption ensures that even if someone intercepts your connection, they can’t read or trace your information back to you.
Secure Your Browser and Devices
Keeping your browser and devices updated is one of the simplest ways to improve your privacy. Software updates often include security patches that protect against new online threats. Outdated systems can make you an easy target for hackers or data leaks.
Here are a few quick tips:
- Always install browser and OS updates as soon as they’re available.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Turn on two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Review browser extensions and remove ones you don’t use or trust.
A well-maintained device is much harder for anyone to spy on or exploit.
Use Privacy-Focused Tools or Features
Some tools are built specifically for privacy. Search engines built for privacy, like Brave, Firefox Focus or DuckDuckGo, block trackers automatically and limit data collection. Pairing these with ad blockers or anti-tracking extensions helps reduce how much of your behavior is monitored online.
You can also use encrypted messaging apps such as Signal or WhatsApp, which protect your chats with end-to-end encryption. Together, these tools keep your browsing, communication and data more secure and less visible to third parties.
Regularly Clear Cached Data and Cookies
Cached data and cookies help websites load faster, but they can also reveal where you’ve been online and allow advertisers to track you. Regularly clearing them keeps your browsing private and prevents personalized tracking.
In Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge, you can find this option under Settings > Privacy and Security > Delete Browsing Data. Choose to delete cookies, cached images and site data. Doing this once every few weeks helps you maintain a clean, private browsing environment.
Does Incognito Mode Leave Any Trace?
Incognito mode hides your local browsing history, cookies and site data from other users on the same device. However, it doesn’t make you completely invisible online. Your IP address remains visible to your ISP, employer or school network, and the websites you visit can still collect information about your activity.
Even when you’re browsing privately, your network administrator can log visited domains through Wi-Fi history or router records. This means someone managing your network can still see what sites were accessed, even if they can’t view specific pages or search terms.
To achieve stronger privacy, it’s best to pair incognito mode with other tools like VPNs, ad blockers and privacy browsers. These can encrypt your connection, mask your IP address and make it much harder for anyone to track what you do online.
Protect Your Privacy With Panda Security
If you want more than just basic incognito protection, Panda Security helps you take real control of your privacy. With Panda Dome VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted and your IP address stays hidden — whether you’re at home, on public Wi-Fi or using your phone. It keeps your online activity safe from hackers, snoops and data-hungry advertisers.
Panda also offers built-in tools that protect your devices from malware, phishing and identity theft, so you can browse and shop online with confidence. Explore Panda Dome plans today to protect your privacy wherever you go.
Incognito History FAQ
Below are answers to some of the most common questions about private browsing, how to see incognito history on an iPhone and what incognito mode really does (and doesn’t) hide.
Is It Possible to Recover Incognito History?
Yes, but only in limited ways. You can recover some traces through DNS cache, router logs or parental control apps. However, most browsers are designed to erase incognito sessions once they’re closed, so full recovery isn’t guaranteed.
Can I See What Websites Have Been Visited on My Wi-Fi in Incognito?
Yes, even if someone browses privately, your router or Wi-Fi network still records the domains visited. Checking Wi-Fi history or router logs lets you see the websites accessed by devices connected to your network, including those in incognito mode.
How Can I Turn On and Off Incognito Mode?
To turn on incognito mode, open your browser and press Ctrl + Shift + N (Windows) or Command + Shift + N (Mac). On mobile, tap your browser’s menu and select New Incognito Tab. To turn off incognito mode, simply close all incognito windows or tabs. On iPhone, you can switch between private and normal tabs through Safari’s Tabs menu.
Is Incognito Mode Safer Than Regular Browsing?
Incognito mode offers more local privacy — it stops your browser from saving cookies, autofill data and browsing history. However, it doesn’t protect your IP address or prevent websites and ISPs from tracking your online activity. It’s slightly safer for shared devices, but for true privacy, using a trusted VPN or privacy-focused browser is a better option.






