Tor vs. VPN (TL;DR):
- A VPN encrypts all your internet traffic and hides your IP address, keeping your online activity private while maintaining good speed and access.
- Tor routes your data through multiple encrypted nodes, making it nearly impossible to trace but much slower and limited in site access.
Online privacy is becoming a major concern — 81% of internet users worry about how companies collect and use their data. To protect themselves, many turn to tools like proxy sites, private browsers or VPNs. Choosing can be tough, so we created a guide comparing the pros and cons of two of the most popular options: Tor and VPN.
What Is Tor?

Tor, short for “The Onion Router,” is a non-profit organization that researches and develops online privacy tools. The Tor browser is a tool that anyone can download for Linux, Mac, Windows and mobile devices.
The Tor browser is primarily used to protect your identity online. It routes your internet connection through a series of servers and encrypts it, making it difficult for anyone to trace where your data is coming from or identify you.
Tor also protects your online privacy by preventing websites and services from tracking your IP address and location, making it less likely for advertisers and data brokers to track information about your online behavior while using Tor.
In September 2025, Tor also released a beta version of a VPN app, aimed at improving mobile privacy and bypassing censorship.
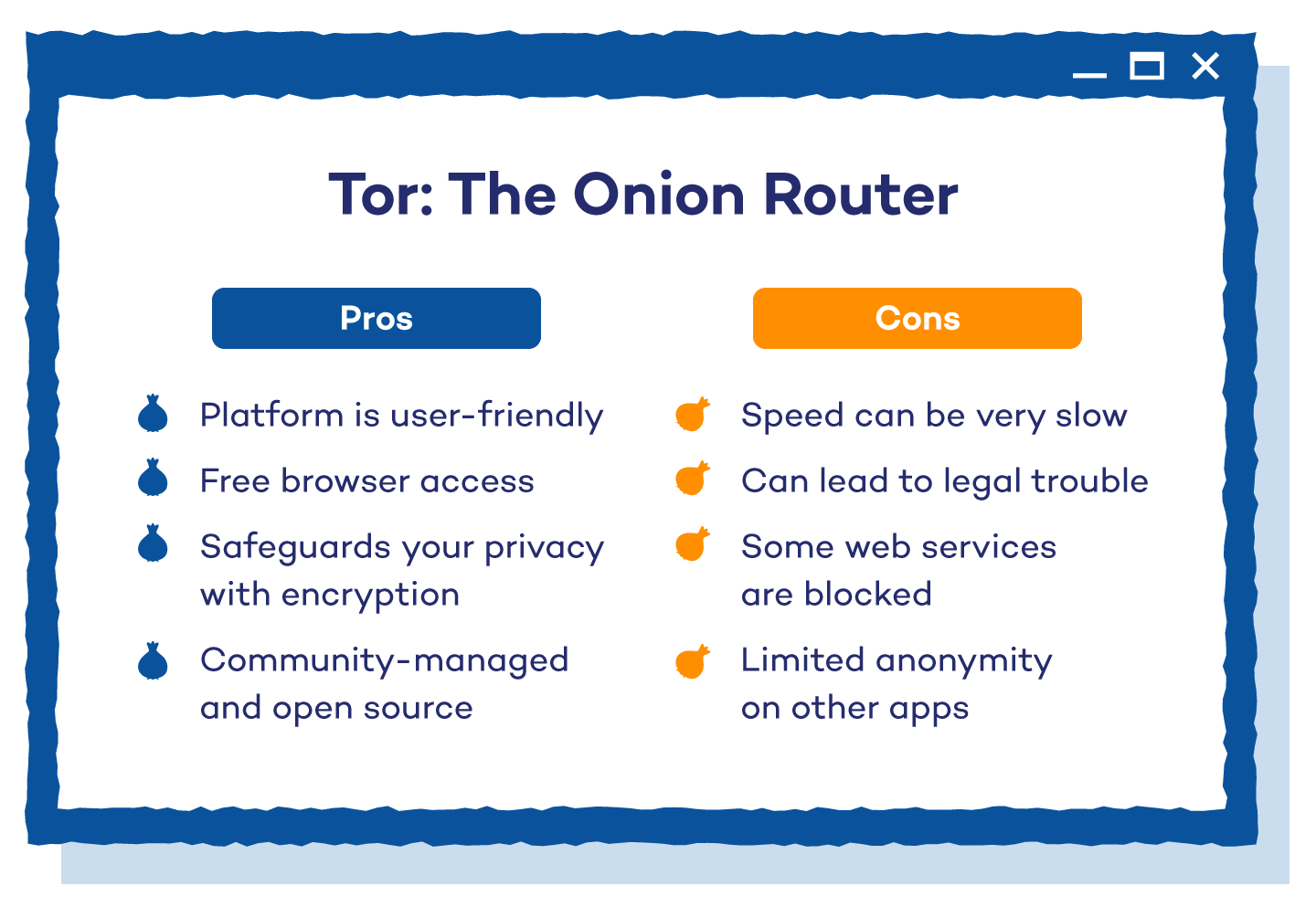
Advantages of Tor
Tor stands apart from other online privacy solutions as a free and easy-to-use option. Advantages of using Tor include:
- User-Friendly: The Tor browser is similar to most browsers you’ve used before. It’s accessible to many people and is easy to use.
- It’s Free: The Tor browser is free to download and use. More advanced users are also able to download the open-source project and make changes to the code as they’d like.
- Safeguard Your Privacy: Tor protects your privacy by not revealing your IP address to the websites you visit. Anyone from journalists and political rebels to your average Joe can use this platform to keep their information safe from repressive governments or big corporations.
- Community and open source: Tor is community-managed and open source, meaning its servers are run by volunteers and its code is freely accessible. This transparency allows peer review, keeps the network secure and makes Tor easy to customize and inspect.
- Compatible: You can use Tor with other web browsers and applications like instant messaging, WeeChat, Thunderbird and Mumble, to name a few. This versatility uniquely positions it as a product that a wide range of users can benefit from.
- Anonymous: With your data traffic routed through multiple servers, you’ll be very hard to track, identify and acquire information from. The layer of encryption Tor adds makes its users anonymous internet dwellers.
 Disadvantages of Tor
Disadvantages of Tor
While it’s an innovative solution for online security, Tor still has some shortcomings to consider:
- Slow speed: Tor can be noticeably slower because your internet traffic is routed through multiple volunteer-run servers. This extra hopping around can make pages, photos and videos take longer to load, especially when fewer people are helping run the network.
- Web services blocked: Many larger web services block access to Tor. When visited, these sites return an error message like a 404. Others allow access but include a maze of CAPTCHAs that are needed to enter the site.
- Legal trouble: Anyone can use Tor, so if illegal activity passes through the network you’re connected to, it could be traced back to you. Governments also monitor Tor users closely, so just using it at all can attract extra scrutiny.
- Limited anonymity with non-Tor traffic: Tor protects only traffic routed through it. Apps or browsers not configured for Tor aren’t anonymized, which can leak information. Proper setup is crucial, and following a Torification guide carefully can help a lot.
Configuring certain applications to work with Tor means your online activity on that app will benefit from the same anonymity and privacy. Applications that aren’t configured to work with Tor don’t benefit from its privacy features.
How Tor Works
Tor disguises your identity online by routing your traffic through multiple servers and encrypting it along the way. Its layers of privacy are like an onion — the more users and servers in the network, the harder it is to trace your activity.
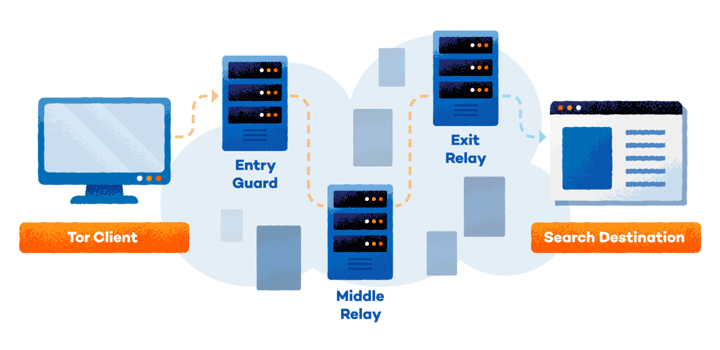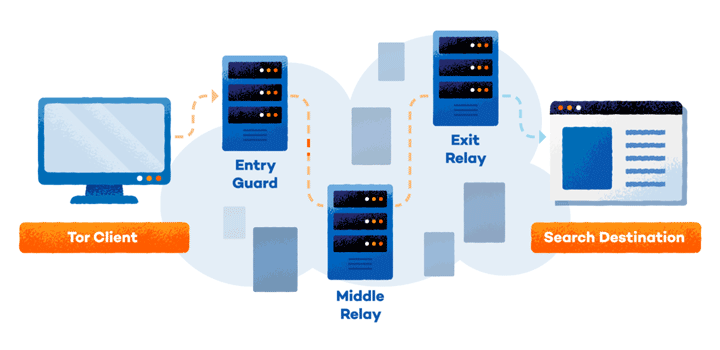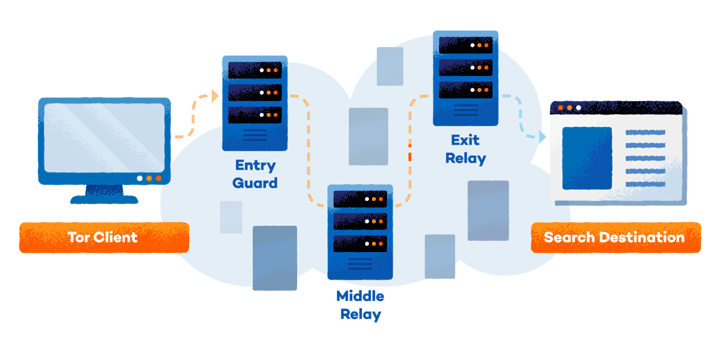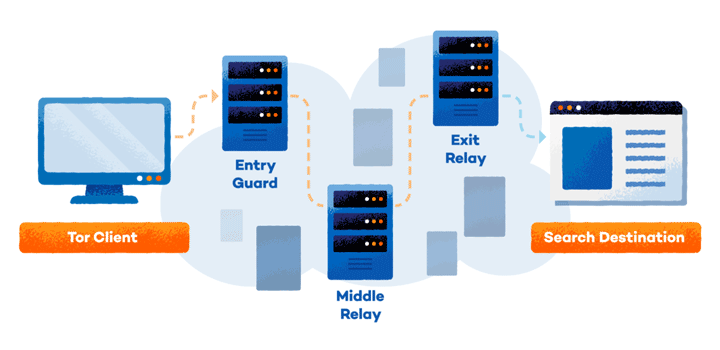
Here’s a quick breakdown of what goes on behind the scenes:
- Middle nodes/relays: These are volunteer-run routers that pass your traffic along the network. Anyone can host these from home.
- End nodes/relays: These are the final servers in the chain that determine the IP address your connection appears to come from. Hosts of end servers can be targeted if illegal activity occurs.
- Bridges: These are hidden Tor servers that are not listed publicly. They bypass IP blocks and help users access Tor in countries that restrict it.
Each node only knows the previous step, so your original IP is hidden. Also, not every user needs to run a node, but more servers means faster and more secure browsing.
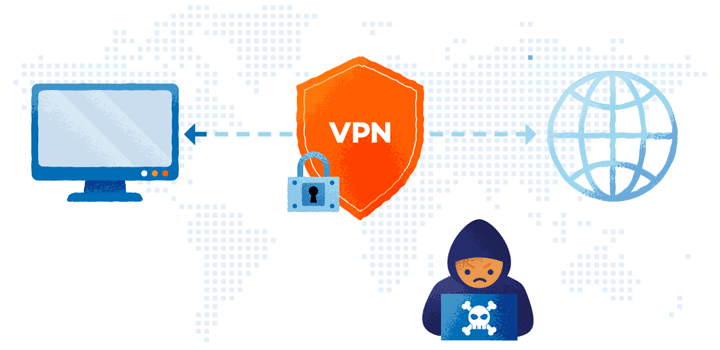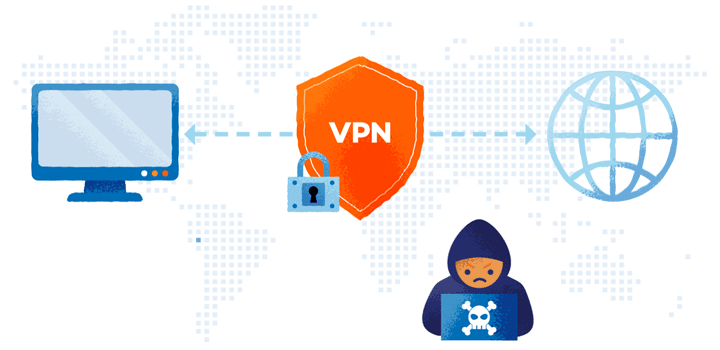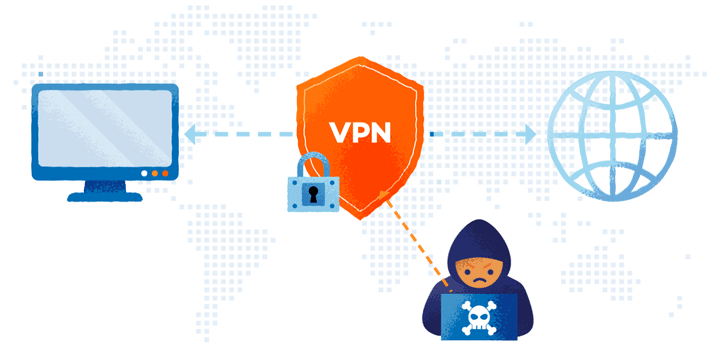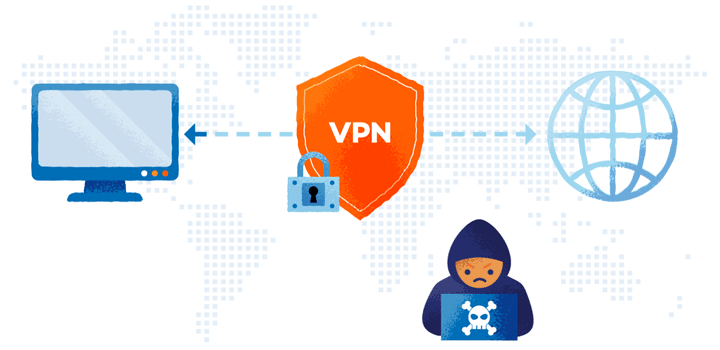
What Is a VPN?

A VPN, short for Virtual Private Network, is software that is able to change your IP address and encrypt your Internet traffic. As of 2025, Security.org reports that 32% of internet users in the U.S. use a VPN, down from 46% in 2024, showing a shift in consumer behavior.
Originally, a majority of VPNs were used by corporations, allowing all employees of the business network to privately access sensitive information. It has now evolved to keep an individual’s online activity private from hackers, government censorship and any other dangers lurking on the internet.
Advantages of a VPN
VPNs offer benefits that make them unique and have set them apart as one of the leading options for online security and anonymity, including:
- Speed: Since you’re only connecting to one server, the internet connection is just as fast as you’re used to. You don’t usually have to wait any additional time for photos or videos to load.
- Accessibility: No matter your geographical location, you have complete access to the internet. Even if a site or service is blocked or changed in your country, you can connect to the version that others see in foreign countries.
- Control of IP address: A VPN protects how you’re seen online. Devices are identified with an Internet Protocol (IP) address that tells their device type, location and online activity. By controlling your IP address, you make it harder for people to identify you.
- Encryption: Unlike Tor, which only encrypts requests while using the browser, VPNs are able to encrypt all the traffic coming from your computer. Top VPNs have also adopted post-quantum encryption protocols to enhance security against future threats.
- Protection against ISP throttling: Some ISPs (internet service providers) throttle or limit internet speeds and bandwidth for specific online activities like streaming. A VPN can bypass those limitations and improve your online experience.
- Versatility: VPNs are versatile enough to be applied on a network level, making them usable with different devices ranging from computers and smartphones to tablets and routers. Some VPNs also provide browser extensions and dedicated platform apps for more customization.
Some top-tier VPNs also include a kill switch, which stops all internet traffic if the VPN connection drops, and multi-hop/double VPN, which routes traffic through multiple servers for extra anonymity.
 Disadvantages of a VPN
Disadvantages of a VPN
Despite its many advantages and huge user base, VPN still has a few shortcomings that you should consider.
- Software failures: For a VPN to work, it needs to run properly. VPN leaks are common if the software isn’t installed and tested properly.
- Costs money: While some VPNs have free options, the more secure versions cost money. There is usually a monthly fee to keep your activity secure.
- VPN provider can see your activity: Some VPN companies log your history while using their service. Look for a statement on your VPN’s website to ensure they aren’t collecting, storing or sharing any permanent identifiers of you.
How a VPN Works
Here’s how a VPN protects your privacy and helps you access restricted content:
- Connect to a VPN server: Your internet traffic is routed through a secure server operated by the VPN provider.
- Change your IP address: This process masks your real IP address, making it appear as though you’re browsing from a different location.
- Access restricted content: By connecting to a server in a country where certain websites or services are available, you can access content that might be restricted in your actual location.
In India, TikTok has been banned since 2020 due to concerns over data privacy and national security. However, if you’re in India and want to access TikTok, you can use a VPN to connect to a server in a country where the app is accessible. This allows you to bypass the geographical restrictions and use the service as if you were in that country.
Tor vs. VPN: Which Is Better?
Both Tor and VPNs protect your online identity, but they do it in different ways. VPNs are usually the more practical choice — they’re faster, encrypt all your traffic and give you full internet access.
Tor, on the other hand, is free and highly anonymous, but slower, limited in site access and can attract unwanted attention from authorities. Your choice depends on what you need most: speed, access or complete online anonymity.
Use a VPN if you:
- Stream, game or download often: VPNs offer fast, stable connections suited for data-heavy activities.
- Use public Wi-Fi: They encrypt your entire internet traffic, keeping hackers from snooping on you in cafes, airports or hotels.
- Want full internet access: VPNs can bypass censorship and geo-blocks, letting you connect as if you were in another country.
- Want an easy setup: Most VPNs come with user-friendly apps for phones, laptops and routers.
- Value all-around security: Premium VPNs add features like a kill switch and multi-hop connections for stronger protection.
Use Tor if you:
- Need maximum or lifesaving anonymity: Tor hides your location through multiple encrypted nodes, making you nearly untraceable.
- Want a free privacy solution: It’s open-source, community-run and doesn’t log your data.
- Are in a high-censorship region: Tor bridges help bypass internet blocks even in countries that restrict VPNs.
- Don’t mind slower speeds: Privacy is the priority here, not performance.
- Are tech-savvy: Tor requires more setup and can be complex for beginners.
In short, choose Tor if you need maximum anonymity and don’t mind slower speeds. Choose a VPN if you want speed, full-site access and strong everyday protection.
Protect Your Data With Panda Security
When choosing a VPN, you want one that’s fast, secure and transparent about how it handles your data. Panda Dome VPN delivers all three. It uses strong encryption to protect your online activity, keeps no logs of your browsing and includes features like real-time antivirus protection to ensure complete security across your devices.
Stay private, stay protected and try Panda’s VPN today for free
FAQ: Tor vs. VPN
Neither Tor nor a VPN provides complete privacy and all security features. Each excels in different areas, so choosing the right solution depends on your goals.
Is Tor Better Than VPN?
Tor is better than a VPN in terms of online privacy and anonymity. The two tools offer a measure of security but excel in different areas. Tor is better for users who are after the highest level of online anonymity, who don’t use it for data-intensive applications and who are willing to trade speed for privacy.
Is VPN Faster Than Tor?
Yes, VPNs are faster than Tor because Tor uses multiple servers/relays to route your connection, whereas VPNs offer a single-hop connection to the server. This means VPNs usually provide a faster internet connection and are more efficient at bypassing ISP throttling.
Is Tor Anonymous?
While Tor isn’t guaranteed to be completely anonymous, it’s designed to offer the highest level of security and anonymity while browsing the web. It’s extremely difficult to track Tor user data and traffic, making it the ideal option for online privacy. That said, many apps and browsers need to be configured to Tor before they’re secure.
Can I Use Both Tor and VPN?
Yes, you can combine them in two ways: Tor over VPN (connect to your VPN first, then use Tor) or VPN over Tor (connect to Tor first, then your VPN). Using both boosts privacy but will slow your connection because your data is encrypted and routed through multiple servers before reaching its destination.






