The online world is vast, fast and unavoidable — a place where connection and creativity thrive, but so does a darker side. Recent cyberbullying statistics reveal that 1 in 5 internet users worldwide are at risk of cyberbullying, harassment or abuse, making this a growing crisis that impacts mental health, safety and self-esteem.
Bullies used to confront their victims in person. Now, they can follow you home through your screen. The digital age has blurred the lines between schoolyards and bedrooms, creating a high-stakes challenge for people worldwide.
Explore 21 alarming cyberbullying statistics that expose the harsh reality behind online harassment — from the definition of cyberbullying to its root causes and hotspots to clear signs you shouldn’t ignore and what you can do to fight back.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Cyberbullying?
- General Cyberbullying Statistics
- Cyberbullying in School Statistics
- Global Cyberbullying and Risk Statistics
- The Role of AI in Cyberbullying
- How to Recognize and Prevent Online Harassment
- Cyberbullying Statistics FAQ
What Is Cyberbullying?
Cyberbullying is the use of electronic communication to bully a person, typically by sending intimidating or threatening messages. It can happen through social media, text messages, online chats and websites.
Here are some of the common examples of cyberbullying include:
- Sharing embarrassing photos or videos of someone online without their permission
- Sending mean or threatening messages
- Spreading rumors about someone online
- Excluding someone from online groupsCreating fake profiles to impersonate or humiliate someone
- Posting hurtful comments or insults on someone’s posts or pages
- Harassing someone repeatedly with unwanted messages or calls
- Using deepfake technology to create manipulated images or videos that damage someone’s reputation
General Cyberbullying Statistics
This section breaks down some surprising cyberbullying facts that show how this issue affects children, adolescents and adults. It’s prevalent across various online platforms and can target individuals based on their physical appearance, personality, gender, race or ethnicity.
1. Fifty-eight percent of netizens say that hate speech is most widespread on Facebook. (Ipsos)
2. Sixty-seven percent of internet users have encountered hate speech online, including 74% of those under 35. (Ipsos)
3. Around 30% of teens report having been cyberbullied at some point in their lives. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
4. About 15% of adolescents across 44 countries have experienced cyberbullying, with rates rising since 2018. Between 2018 and 2022, the share of boys admitting to cyberbullying others climbed from 11% to 14%, while girls increased from 7% to 9%. (WHO)
5. Boys are more likely to be targets of cyberbullying than girls (36.6% vs. 28.6%) and are also more likely to be cyberbullies (21.7% vs. 10.4%). (Cyberbullying Research Center)

Cyberbullying in School Statistics
Cyberbullying within schools is a widespread concern, impacting students’ well-being and academic performance. Monitoring social media activity and implementing comprehensive prevention strategies are essential in addressing this issue.
Here are some key cybersecurity statistics related to schools and students:
6. Fifty-eight percent of students reported experiencing cyberbullying at some point in their lives. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
7. About 33% of students said they had been cyberbullied in the most recent 30 days. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
8. When asked about cyberbullying in the past 30 days, students most commonly reported mean names or comments online (15.7%), exclusion from group chats (20%), and online embarrassment or humiliation via hurtful comments (17%). (Cyberbullying Research Center)
9. In a 2023 survey, 24.2% of boys and 28.6% of girls reported being cyberbullied within the last 30 days. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
10. More than 60% of students who encountered cyberbullying reported that it significantly impacted their learning and sense of safety at school. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
11. Ten percent of students admitted to skipping school at least once in the past year due to cyberbullying. (Cyberbullying Research Center)

Global Cyberbullying and Risk Statistics
Cyberbullying doesn’t play favorites — it targets all ages, and adults aren’t immune. The emotional fallout ranges from anxiety and depression to more serious risks like suicide. Tackling this requires stronger prevention, smarter digital citizenship and a global push to make online spaces safer for everyone.
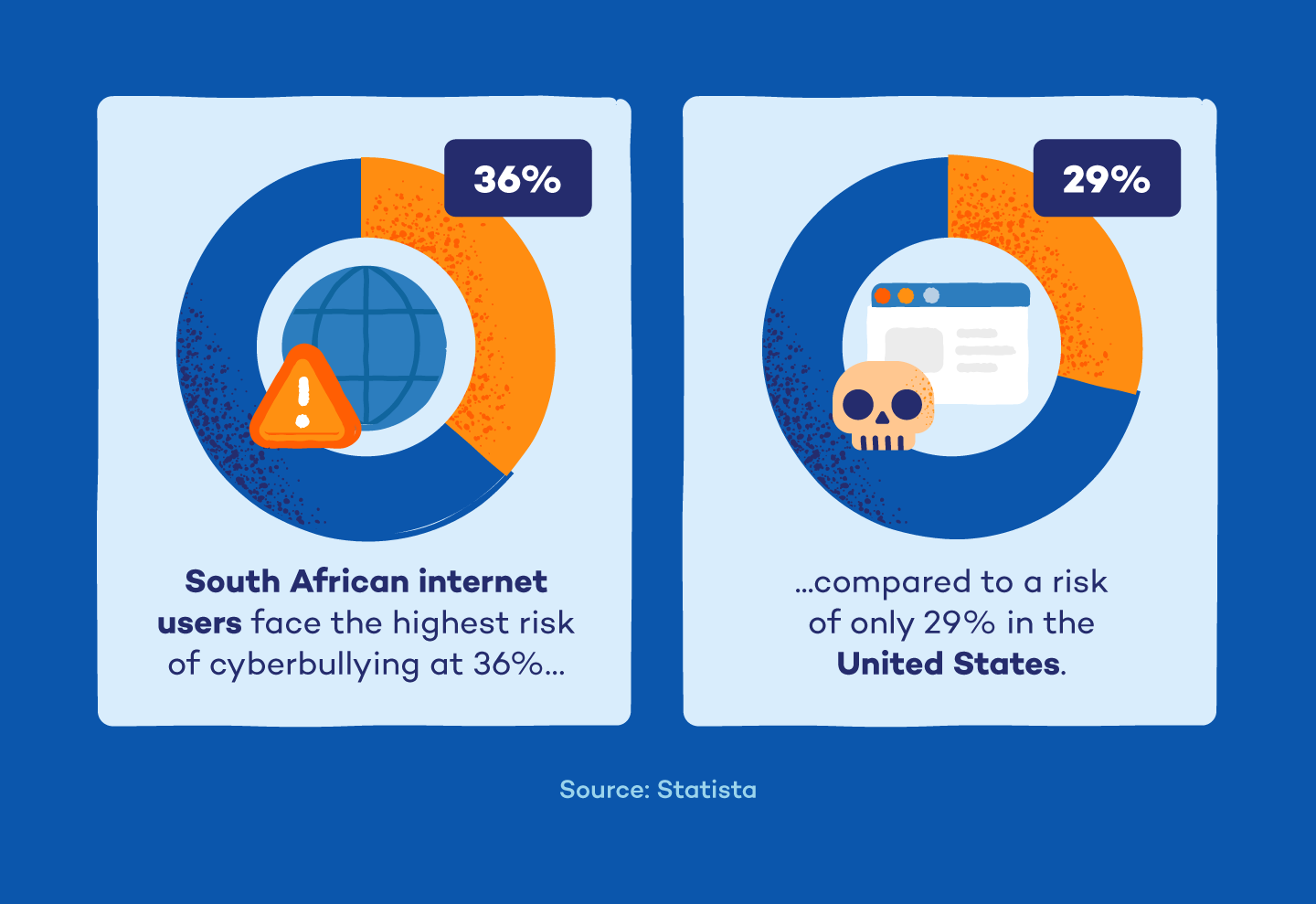
12. South African internet users face the highest risk of cyberbullying, with 36% exposed to online harm. (Statista)
13. In France, only 10% of internet users reported being at risk of cyberbullying. (Statista)
14. Almost half (49%) of internet users in Singapore worry about exposure to cyberbullying. (Statista)
15. Teenagers with high online addiction are twice as likely to experience cyberbullying compared to those with low addiction levels. (Statista)
16. In the U.S., 77.5% of school students reported experiencing negative or hurtful online posts about themselves, and 70.4% of students reported rumors being spread about them online. (Statista)
17. Twenty-five percent of Canadian users avoid social media or online discussions due to fear of harassment. (Statista)
The Role of AI in Cyberbullying
AI is changing the game in cyberbullying — both as a tool for harm and a weapon against it. On one hand, AI can be used to create fake images, videos (deepfakes) and messages that deepen emotional damage and spread harassment faster than ever. On the other hand, many platforms rely on AI-driven moderation to spot and remove millions of bullying posts every month.
The following facts about cyberbullying show just how widespread the problem is:
18. Between April and June 2024, Facebook removed 7.8 million pieces of bullying and harassment content. (Statista)
19. Instagram removed over 10 million pieces of bullying and harassment content in the same period. (Statista)
20. In the first half of 2024, X (Twitter) suspended 1 million accounts for abuse, harassment and hateful content, and removed 2.2 million pieces of content. (Statista)
21. Snapchat reported over 6.6 million bullying and harassment violations in the first half of 2023. (Statista)
How to Recognize and Prevent Online Bullying
It’s important to be aware of the types of cyberbullying to avoid becoming one of the cybersecurity statistics. If you suspect your child is engaged in one or more of the following behaviors, it’s time to take action and protect your child from cyberbullying.
- Flaming: Online arguments that take place within DMs and messaging apps, oftentimes with vulgar behavior to provoke another person
- Harassment: Sending offensive messages repeatedly, including verbal abuse and unsolicited sexual content
- Denigration: Distributing derogatory or false information about someone to damage their reputation
- Cyberstalking: Repeatedly sending threatening messages in an attempt to intimidate someone; in some cases, this behavior is illegal
- Masquerade: Creating a fake account pretending to be someone else, sometimes even stealing credentials and posting embarrassing or vicious content
- Trolling: Deliberately posting inflammatory, off-topic or hurtful comments online to provoke emotional reactions or disrupt conversations
- Deepfaking: Using AI to create convincing but fake videos, audio (voice cloning) or images of someone, often to embarrass, harass or spread false information
Notable warning signs of cyberbullying can include withdrawing from social activities, avoiding school, dropping grades or appearing anxious or sad after going online. In some cases, cyberbullying is illegal. In less severe cases, blocking the perpetrator and contacting a school administrator is the best course of action. Be proactive as a parent — keep parental controls on and set a media agreement with your children.

Protect Your Family Online With Panda Security
Online harassment doesn’t discriminate — anyone can be a target, including members of the LGBTIQ+ community who often face unique digital security challenges. Protecting your family means safeguarding not just devices but emotional well-being and personal identity.
Panda Security offers advanced protection to detect, block and prevent cyberbullying, identity theft, phishing scams and other online threats. With tools for parental controls, social media monitoring and privacy protection, Panda helps you take a proactive stance against harassment.
Don’t leave your loved ones vulnerable. Give them the confidence to explore the internet safely with Panda Dome Family.
Additional Resources
It’s distressing to see how many people get cyberbullied in a year. Here are some cyberbullying prevention resources that have additional information for suicide prevention, healthy technology habits and articles with practical parental advice:
- National Crime Prevention Council
- StopBullying.gov
- Technology and Youth: Protecting Your Child From Electronic Aggression
- Stomp Out Bullying
Online bullying is a problem that will persist as technological advances continue. Be aware of your children’s internet use and download proper parental controls to handle and prevent cyberbullying effectively.
Cyberbullying Statistics FAQ
Cyberbullying is constantly evolving, and with the rise of AI, the way people connect — and harm — online is changing, too. From AI-generated deepfakes to automated harassment, the future of AI will shape both the risks we face and the tools we use to protect ourselves.
This FAQ answers the most common questions about cyberbullying, blending facts with insights on how technology and emotional connections to AI influence online behavior.
How Many Kids Get Cyberbullied Each Year?
In 2025, the Cyberbullying Research Center found that 58% of students between the ages of 13 and 17 in the U.S. have experienced cyberbullying in their lifetime.
Which Country Has the Highest Rate of Cyberbullying?
According to Statista, South Africa leads the world, with 36% of internet users exposed to online harm. The United States and India follow at 29%.
What Age Group Has the Highest Rate of Cyberbullying?
The age group with the highest rate of cyberbullying tends to be adolescents and young adults, typically between 12 and 17 years old.
What Are the Top 3 Social Media Platforms Students Are Cyberbullied On?
According to StopBullying.gov, cyberbullying most often takes place on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat and TikTok, where users interact publicly and privately. These platforms make it easy to spread harmful messages, rumors or threats quickly and widely.
What Are the Most Common Forms of Cyberbullying Among Kids Today?
According to The University of British Columbia, the most common forms of cyberbullying include name-calling, threats and nasty comments about someone’s appearance. It usually happens through texts, messaging apps and social media, but can also show up in emails, online games and video-sharing platforms.
What Percentage of Teens Experience Cyberbullying?
A recent survey by the Cyberbullying Research Center shows that 32.7% of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 have experienced cyberbullying in the last 30 days.