A network security key is simply the password for your Wi-Fi. It lets authorized devices connect to your network and keeps your data safe from outsiders.
According to recent survey data, 86% of people have never changed their router’s admin password, and over half have never touched the factory settings. That means millions are still using the default details printed on the back of their routers — details hackers also know.
This is where your network security key comes in. It’s the digital lock that keeps strangers off your Wi-Fi and protects your data while you browse, stream or shop online. Learn what a network security key really is, how to find it, how to change it and why doing so matters for your online safety.
What Is a Network Security Key and How Does It Work?
A network security key is a fancy name for your Wi-Fi password. It lets you join the network securely, keeping everything you send private. The key ensures only the right people get in and that their data stays safe once inside. Two processes come into play here: authentication and encryption.
Authentication: Proving Who You Are
When you type in the network security key to connect your phone or laptop, the router checks if the code matches. If it does, you’re in. If not, access denied. This stops strangers from joining your Wi-Fi without your approval. Without authentication or a password, anyone within range could use your Wi-Fi and even snoop on your activity.
Encryption
Once you’re in, the key also sets up encryption, which scrambles your data into unreadable code while it travels between your device and the router. Even if someone intercepts it, all they’d see is a mess of characters. Only devices with the correct key can unscramble that data back into something useful.
4 Types of Network Security Keys
Over the years, Wi-Fi security has evolved to keep up with new threats. Different standards have been developed, each with its own level of protection. Here are the four main types you’ll come across:
| Security standard | Encryption strength | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| WEP | Weak | Outdated and rarely used today |
| WPA | Moderate | Better than WEP, but now outdated with known vulnerabilities |
| WPA2 | Strong | Safe and reliable for most modern networks |
| WPA3 | Very strong | Latest standard; most secure, but not all devices support it yet |
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
WEP was one of the first security systems for Wi-Fi. It uses a simple encryption method, but it’s now considered very weak. Hackers can break into a WEP-protected network in minutes, which is why it’s rarely used now. If your Wi-Fi still uses WEP, you should update to a newer standard.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
WPA replaced WEP in 2003 and offered stronger security by adding better encryption methods. It was a big step forward at the time, but today it’s also outdated. While still more secure than WEP, WPA has known vulnerabilities and shouldn’t be your first choice if newer options are available.
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2)
WPA2 is one of the most widely used security standards. It introduced even stronger encryption, making it much harder for hackers to crack. Most modern routers and devices support WPA2, and it’s considered a safe and reliable option for protecting your network.
Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3)
WPA3 is the latest and most secure version. It builds on WPA2 with tougher encryption and better protection against password guessing. WPA3 is designed to keep your network safe even as hacking methods get more advanced. While not all devices support it yet, it’s the gold standard for Wi-Fi security moving forward.
How to Find Your Network Security Key on Your Router
To find your network security key, you can either check the physical router itself or log into its settings through a web browser. Here are the steps you can follow.
Method 1: Check the Router Sticker
- Locate your Wi-Fi router.
- Look for a sticker on the back, bottom or side of the device.
- On the label, you should see details like service set identifier (SSID) or network name, username and password.
- The password is your network security key.
If the password has been changed from the default, the sticker may not match. In that case, you’ll need method 2.
Method 2: Log in Through a Web Browser
- Open a web browser.
- In the address bar, type your router’s IP address — often something like 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1. You can find it in your device’s network settings.
- Press Enter.
- Log in to your router’s admin panel.
- The default username is often admin.
- The default password is often admin or password.
- These may also be printed on the router label.
- Once inside, navigate to the Wireless Settings or Wi-Fi Settings section.
- Find your Wi-Fi network.
- Look for the Password, Network Key or Security Key field.
This password is your current network security key. Sometimes it may appear hidden behind asterisks, with an option to Show.
Heads-up:
Router interfaces and menu names can vary depending on the brand and model, so the exact steps may look a little different for you.
How to Find Your Network Security Key on Your Devices
You don’t always have to log into your router to find your network security key. Most phones and computers store it for you once you’ve connected to Wi-Fi. Here’s how to locate it on Android, iPhone, Windows and macOS devices.
How to Find the Network Security Key on Android
On Android devices, there can be two network security keys based on the network you use:
- When you’re using Wi-Fi, it’s the Wi-Fi password saved on your phone for the network you’re connected to.
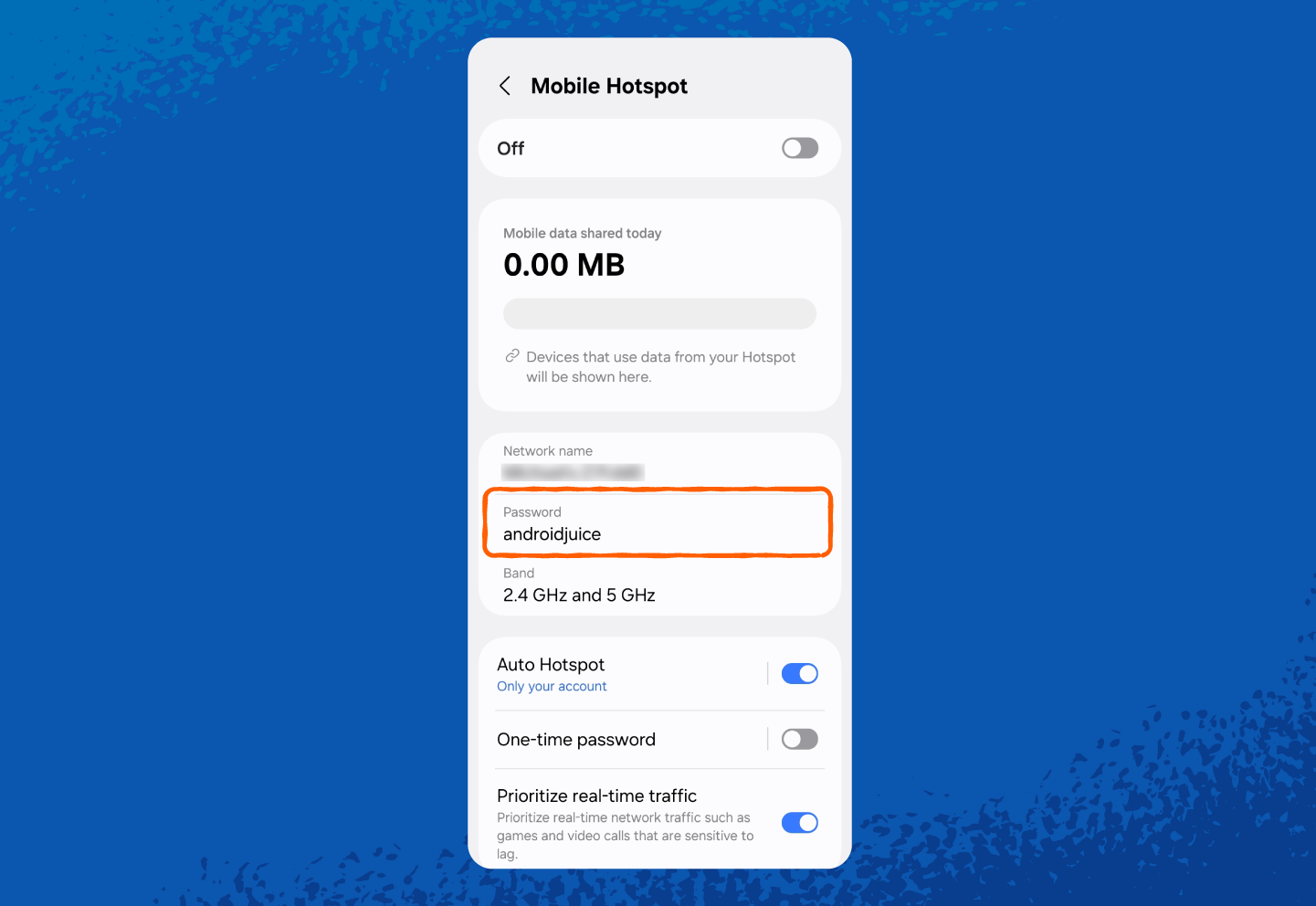
- When you’re using your phone as a hotspot, it’s the hotspot password that other devices use to connect to your phone’s internet.
Here’s how to find your Wi-Fi network security key on Android:
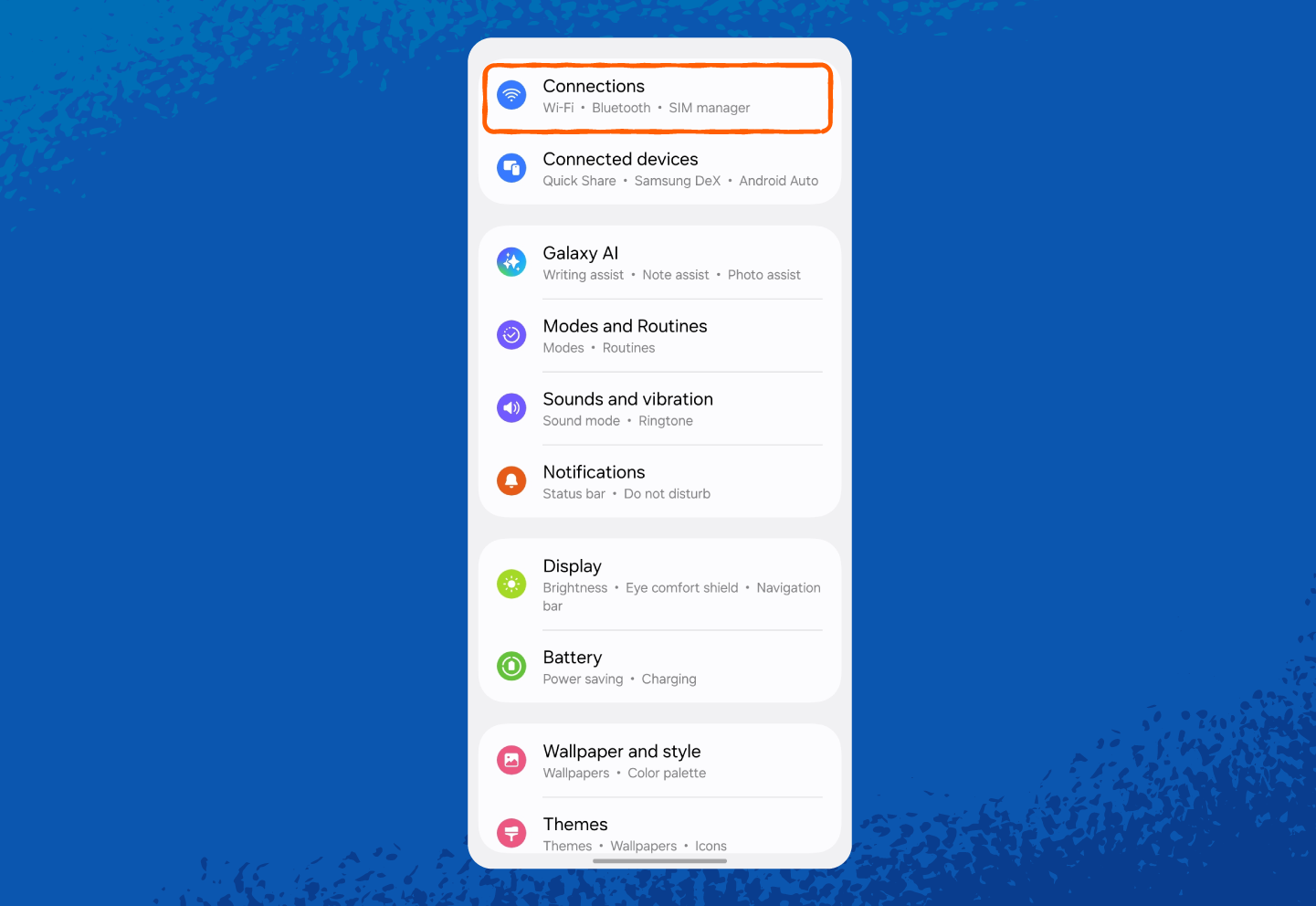
1. Open Settings.
2. Tap Connections or Network & Internet (wording may vary by phone model).
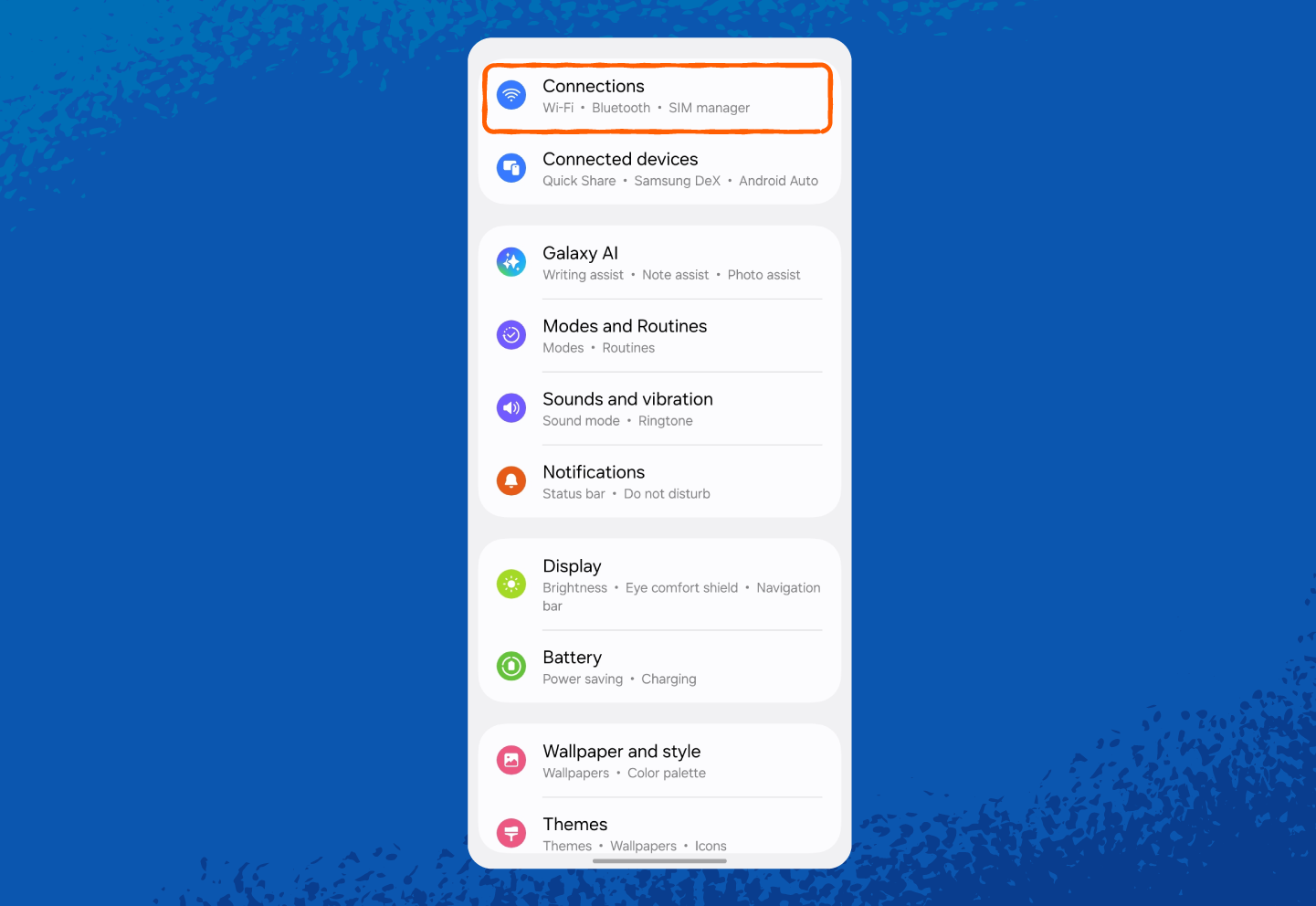
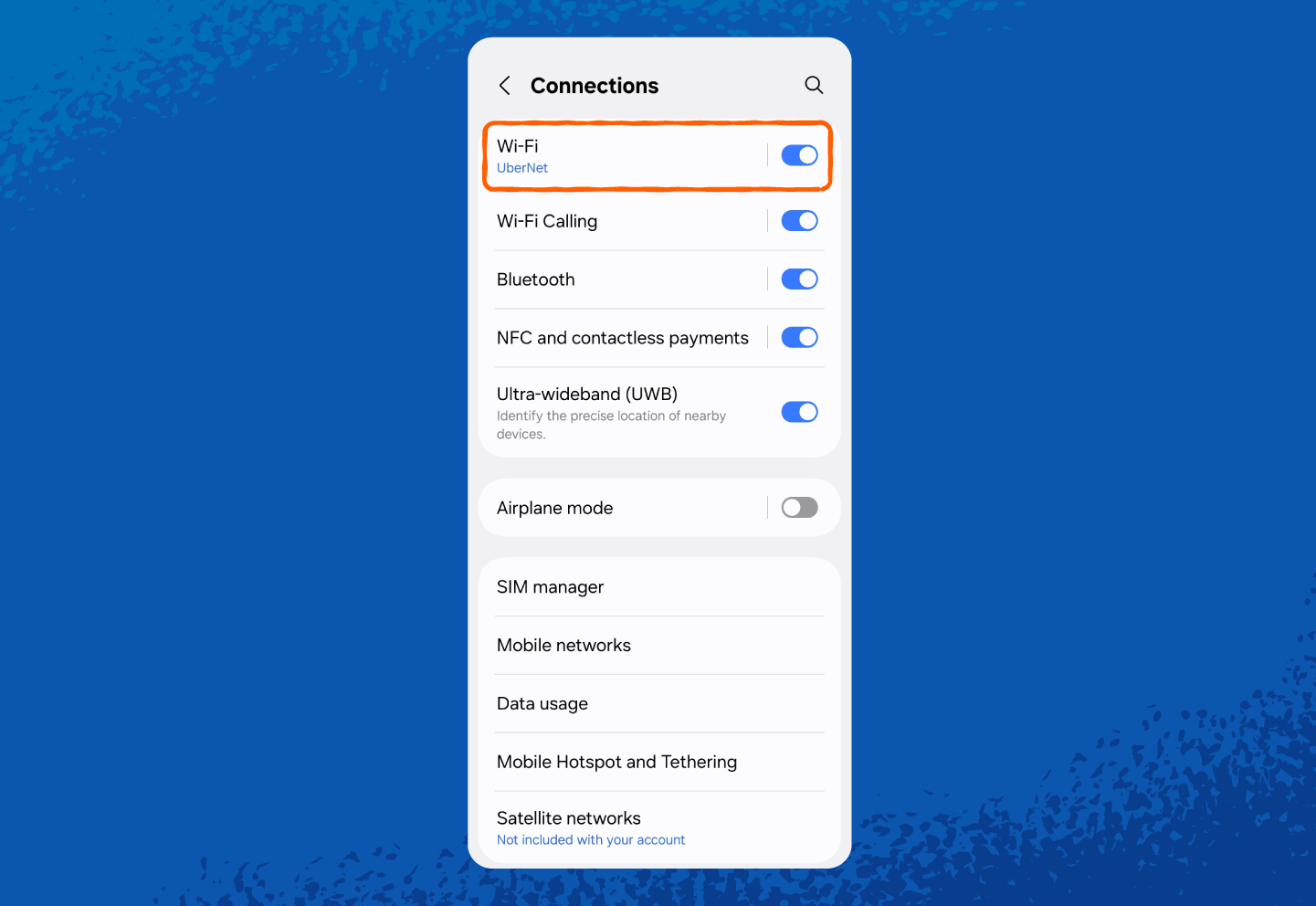
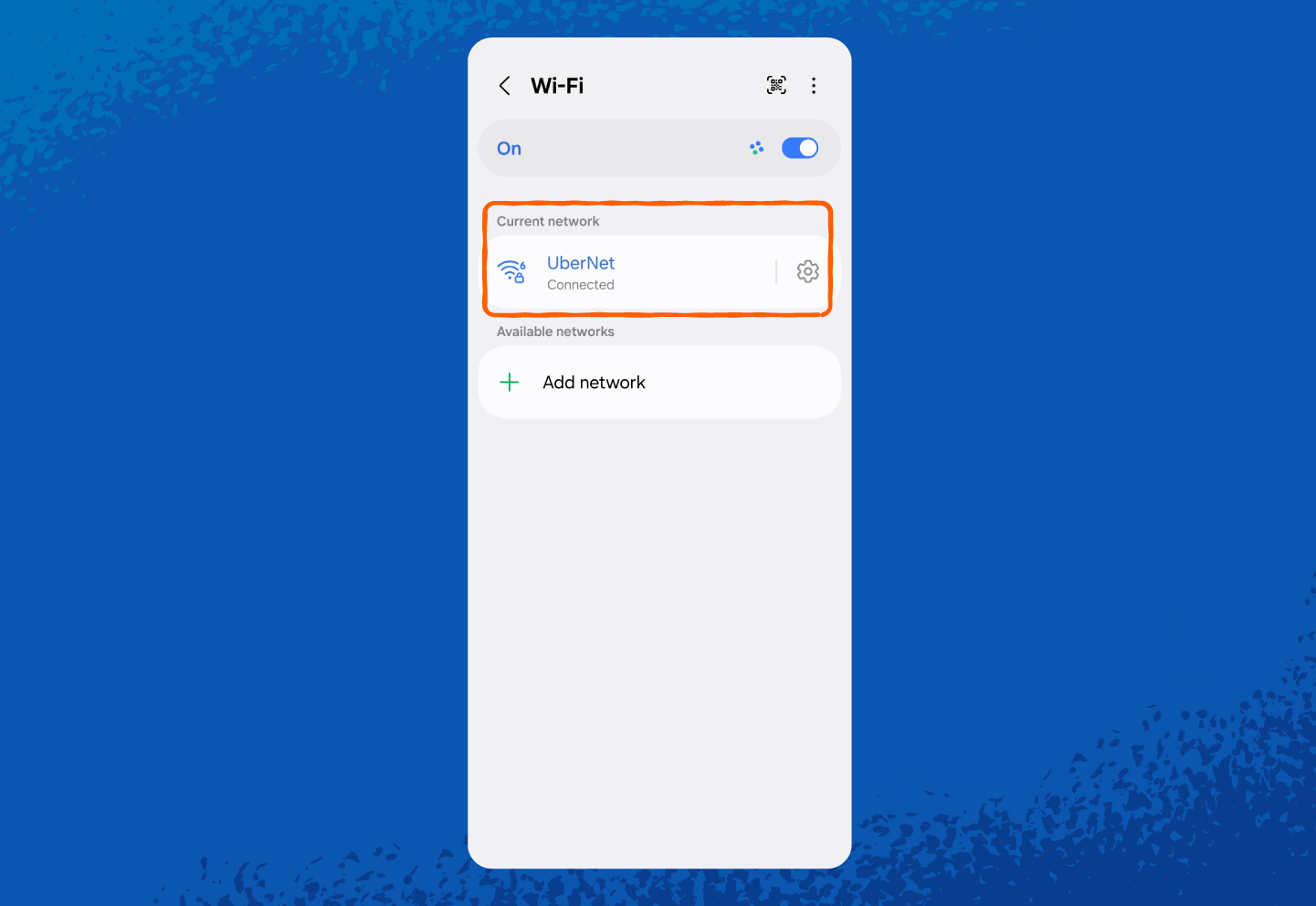
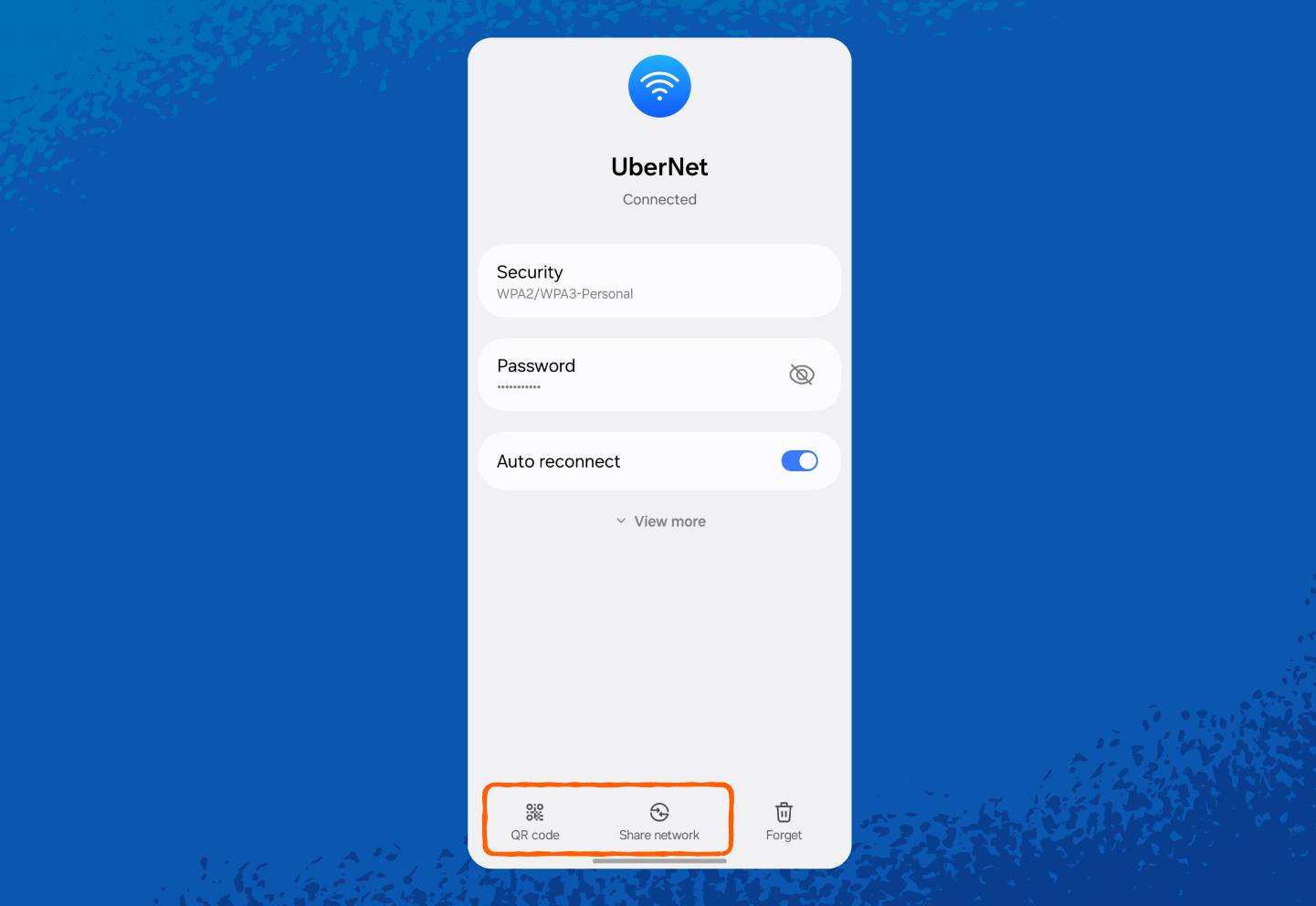
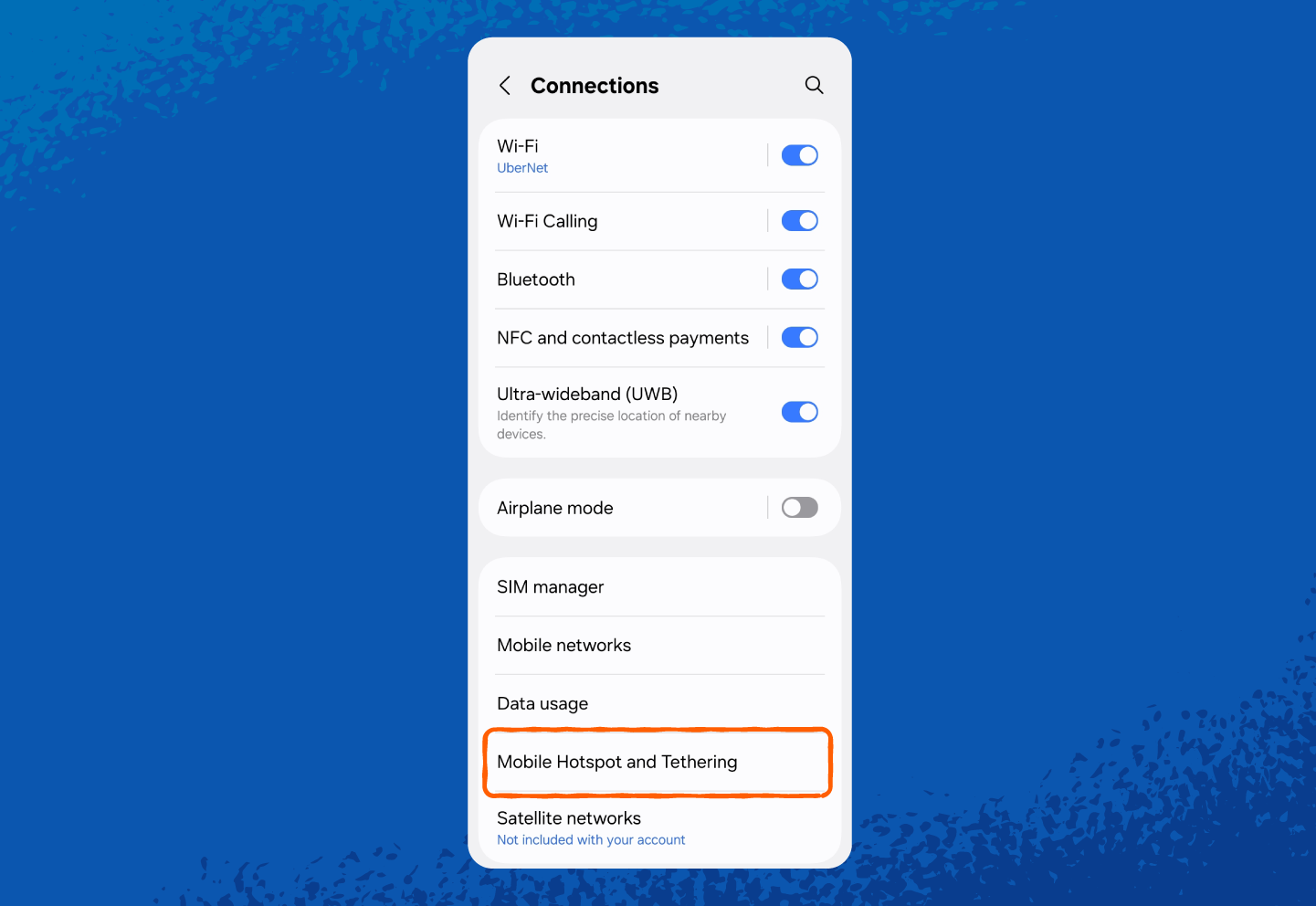
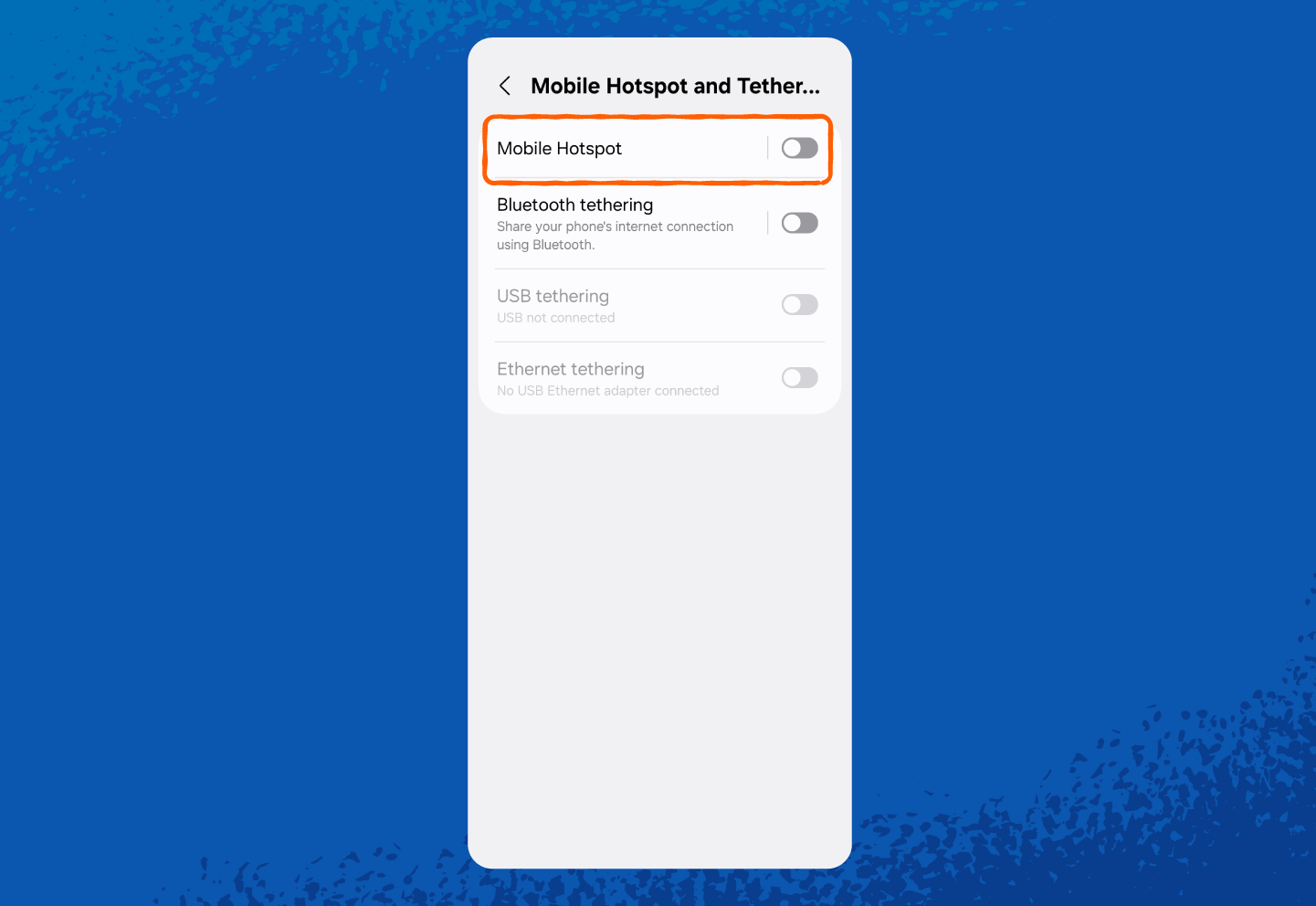
And here’s how to find your hotspot network security key on Android:
1. Open Settings.
2. Tap Connections or Network & Internet (wording may vary by phone model).
How to Find the Network Security Key on iPhone
Just like Android, your iPhone has two types of keys:
- For Wi-Fi, it’s the Wi-Fi password you’ve entered for the network you’re connected to.
- For your hotspot, it’s the password other devices use to connect to your iPhone’s hotspot.
Here’s how to find your Wi-Fi network security key on iPhone:
1. Open Settings.
2. Tap on Wi-Fi.
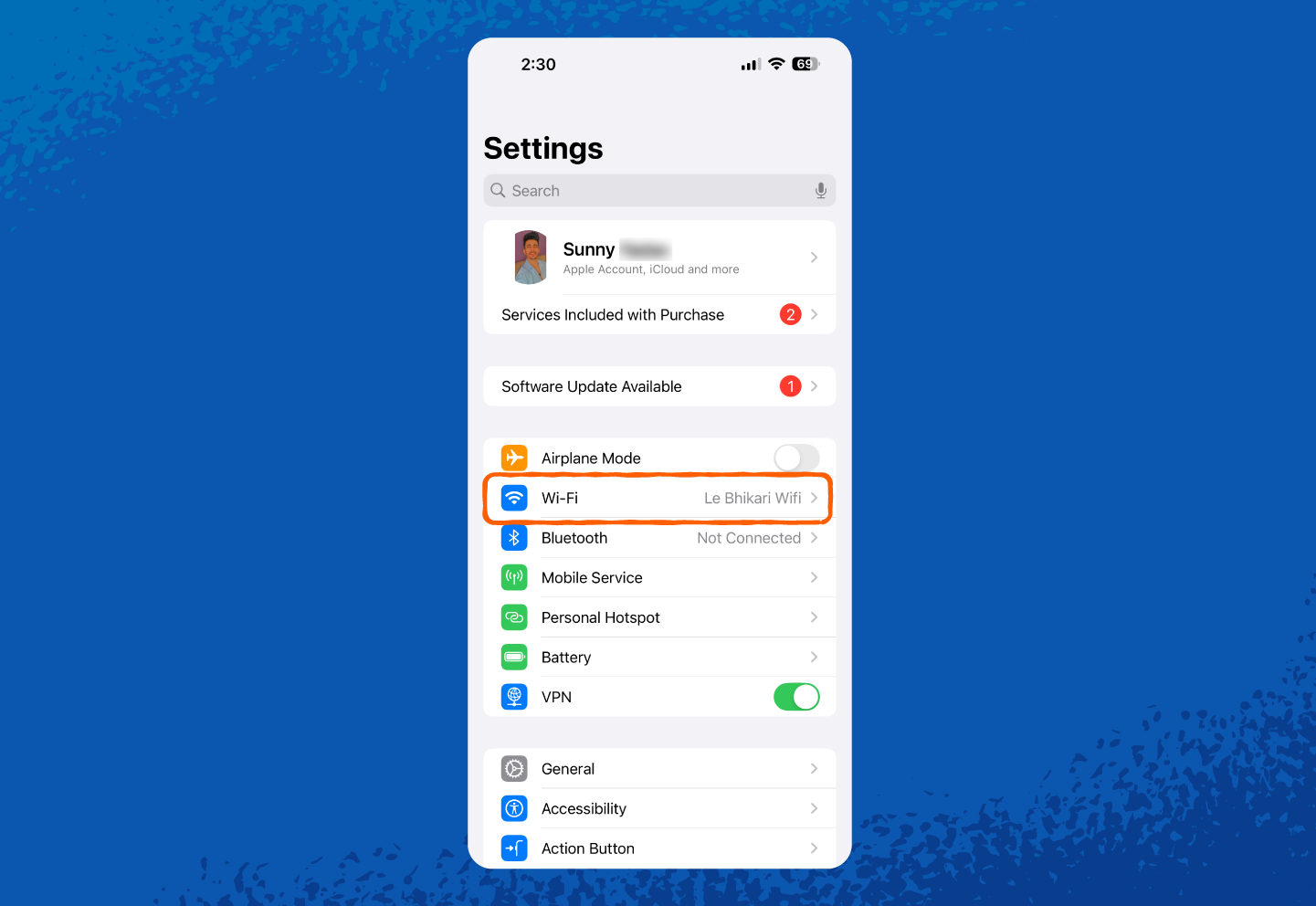
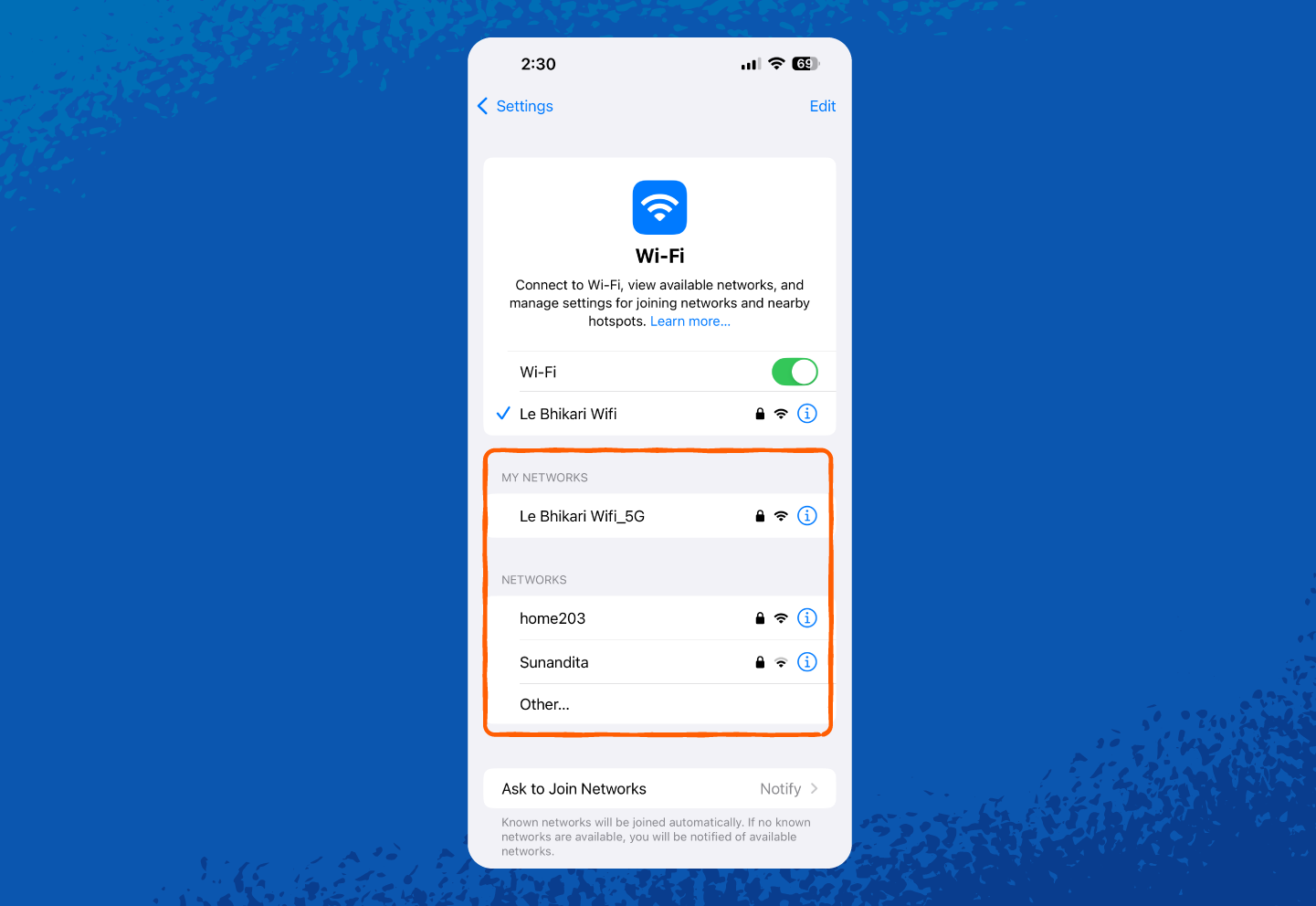
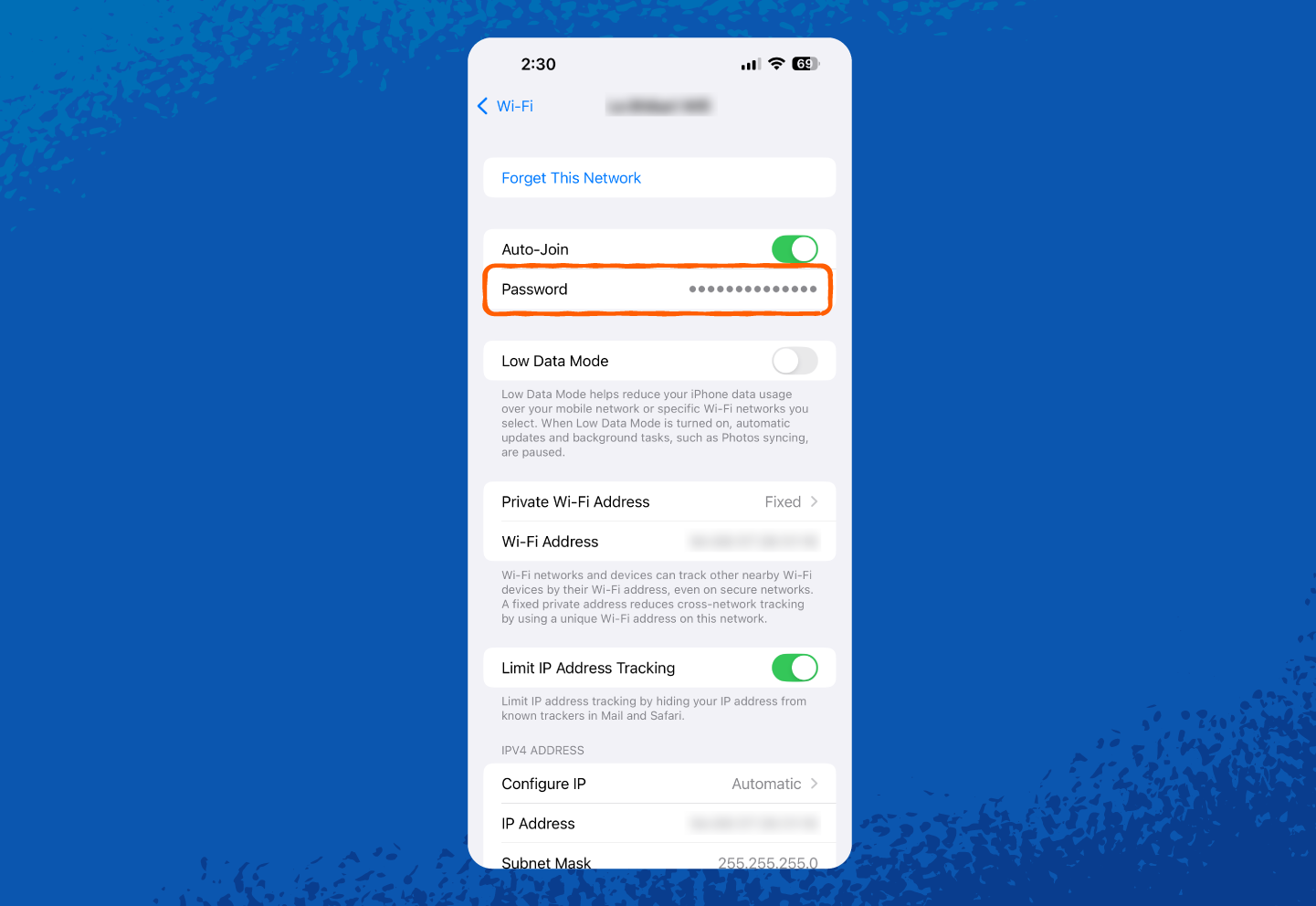
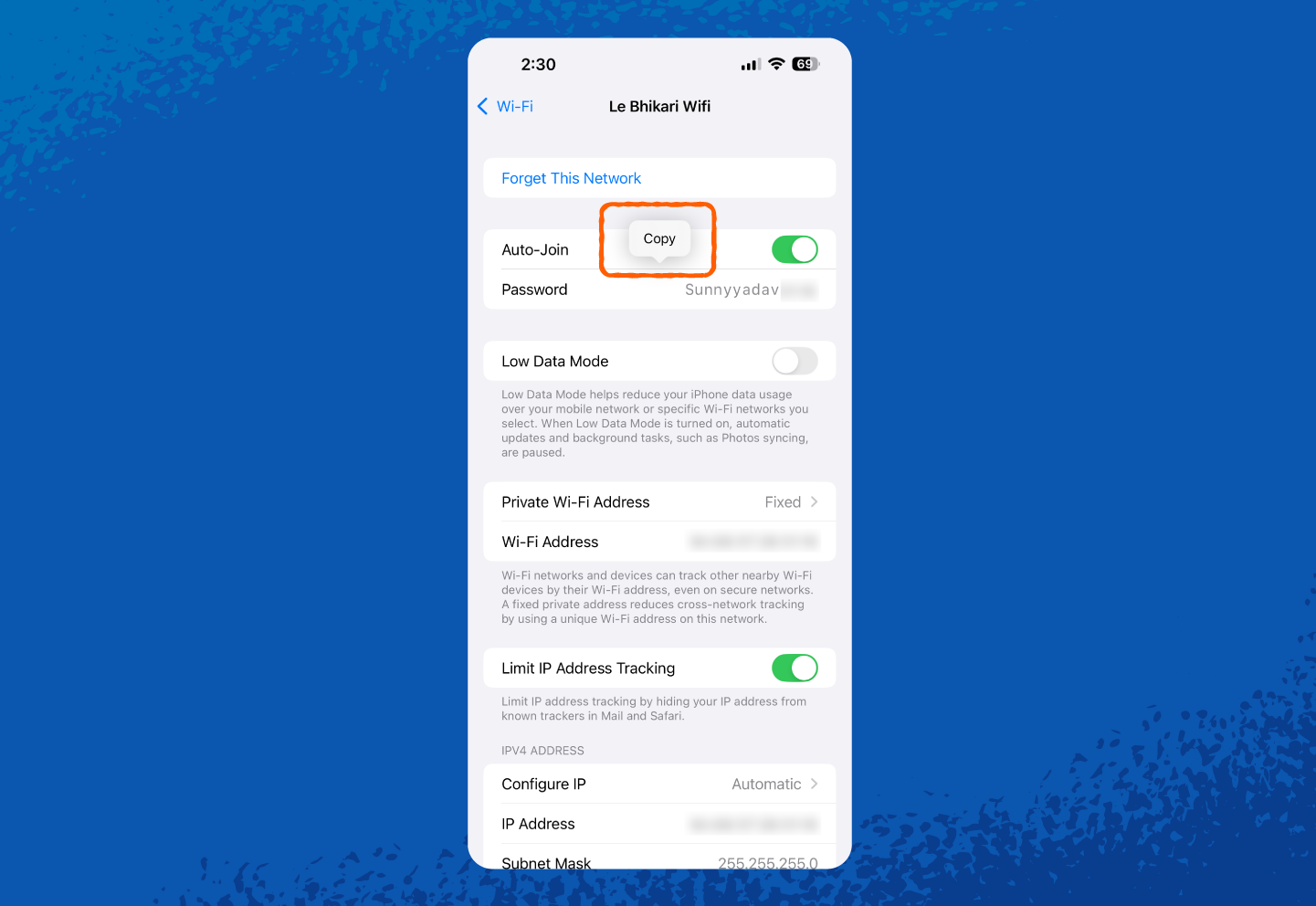
6. Once unlocked, you can see or copy your network security key.
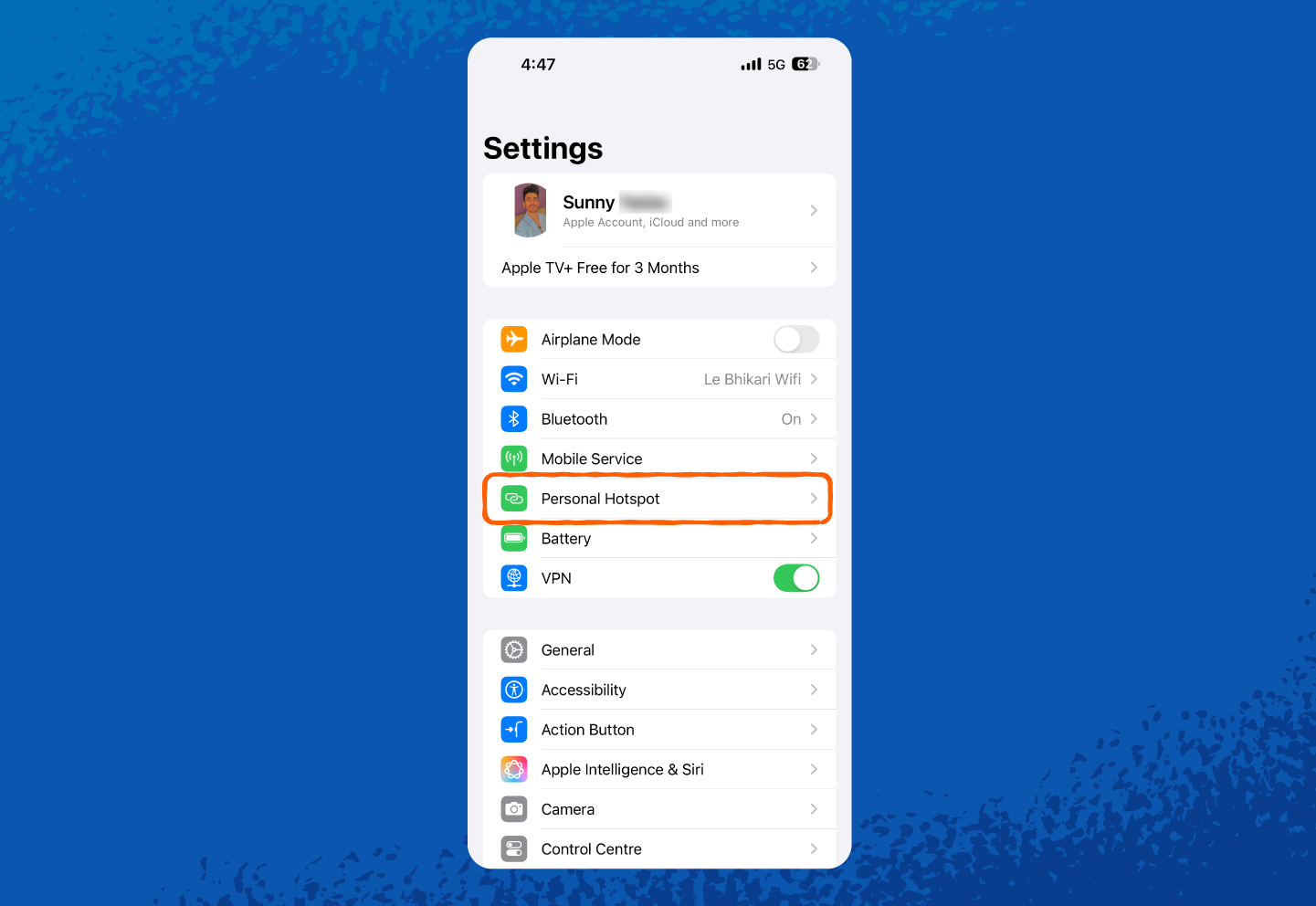
1. Open Settings.
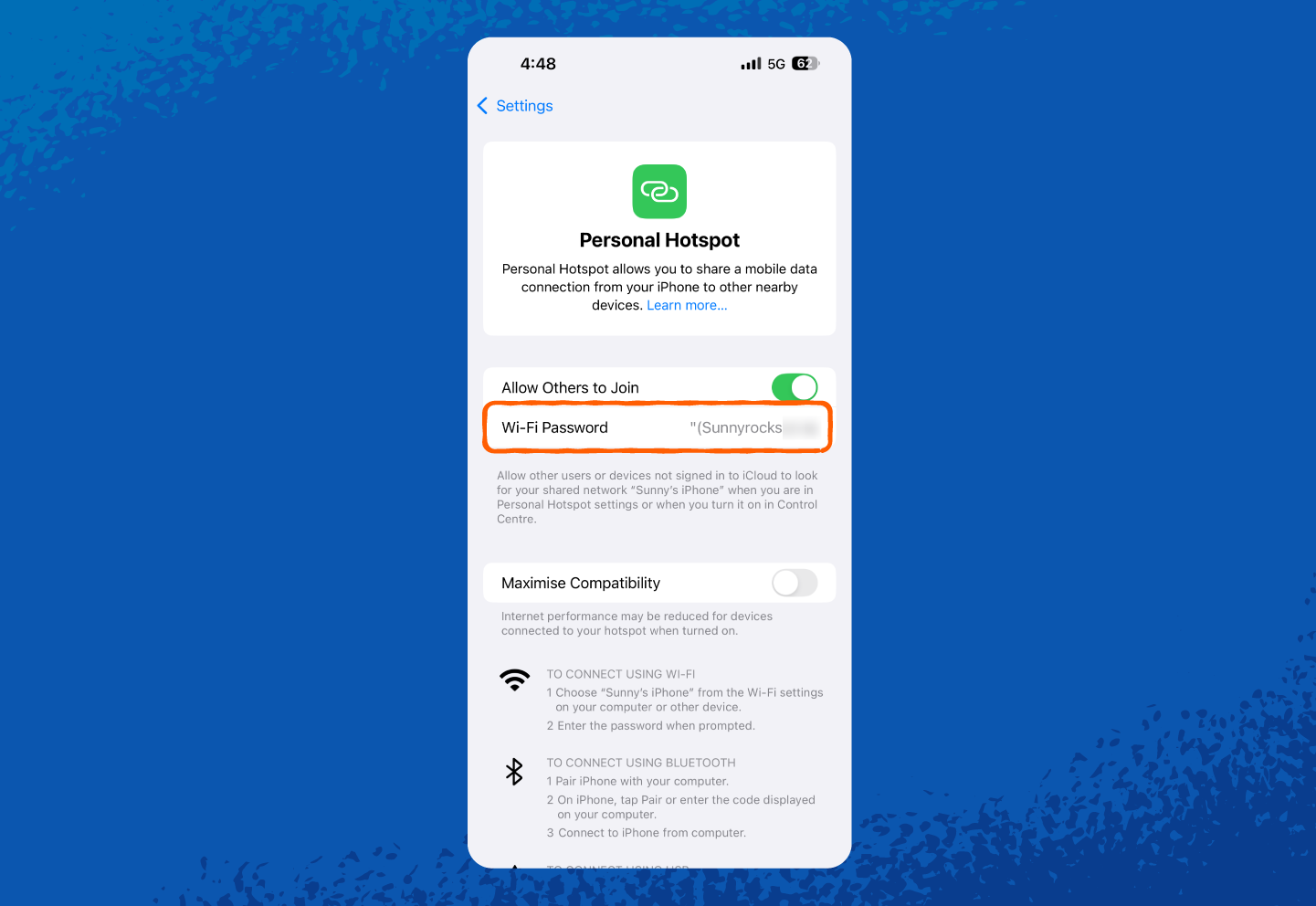
2. Tap Personal Hotspot (or tap Cellular first, then Personal Hotspot, depending on your iOS version).
How to Find the Network Security Key on Windows
If your Windows computer is already connected to the Wi-Fi, you can pull up the saved network security key by following these steps:
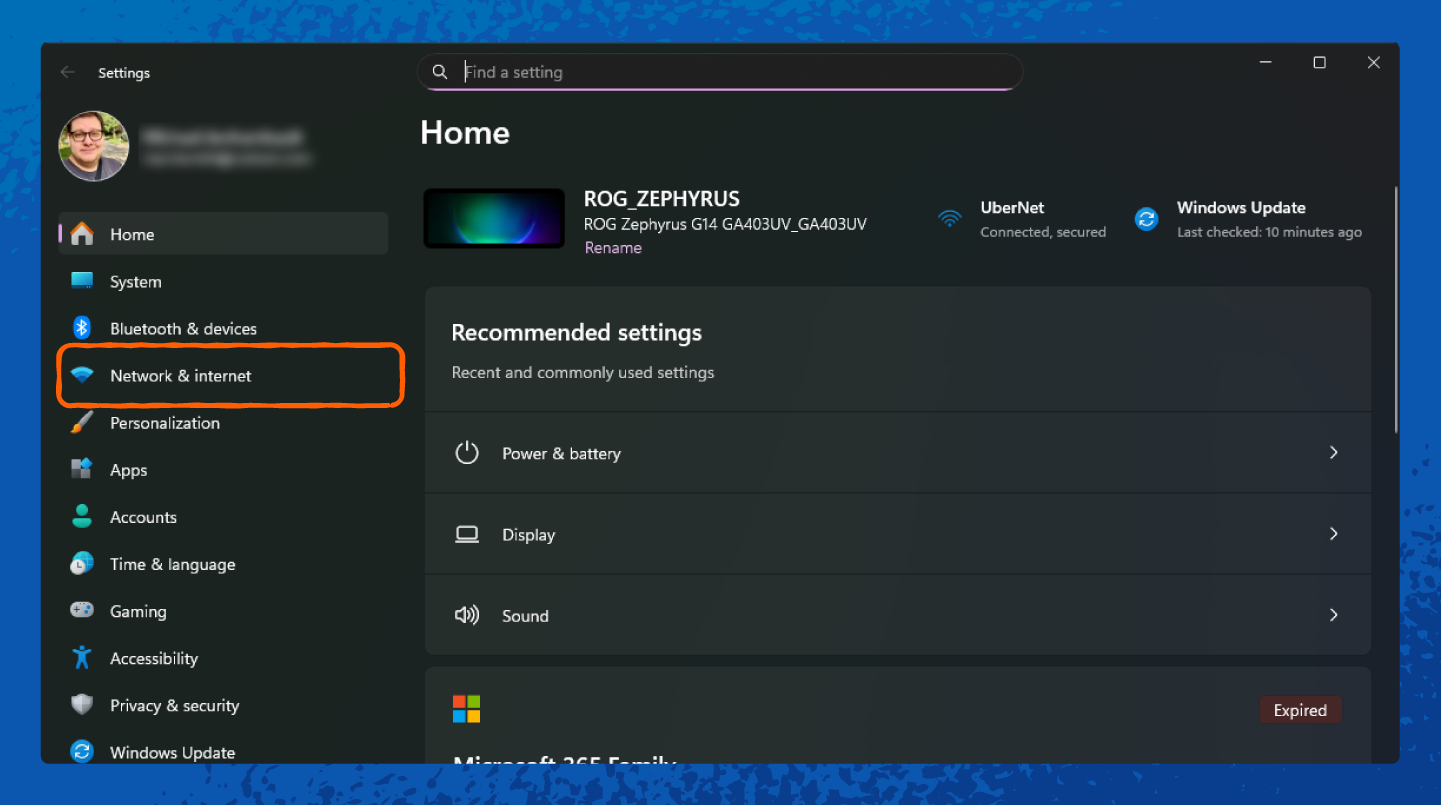
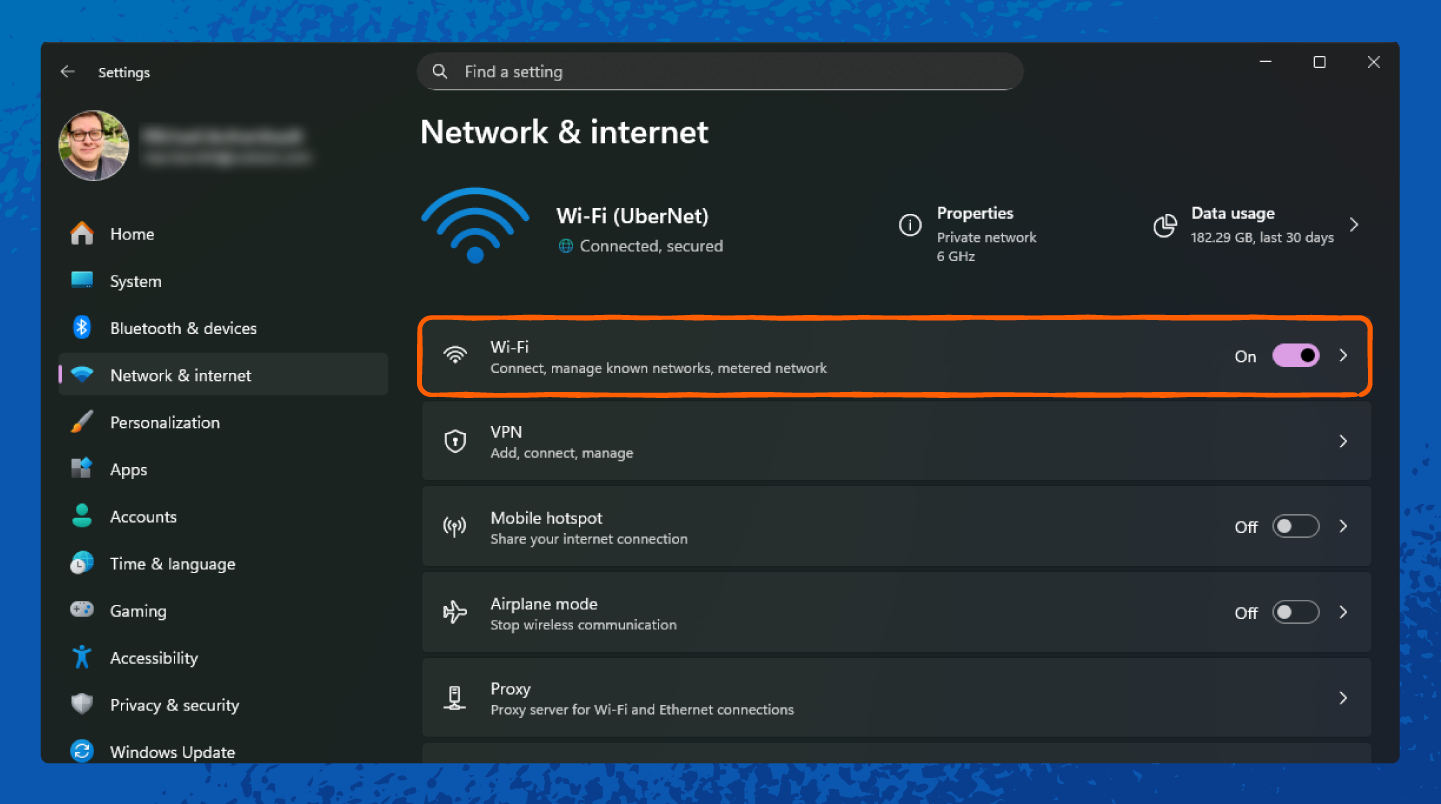
1. Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the taskbar and select Network & internet.
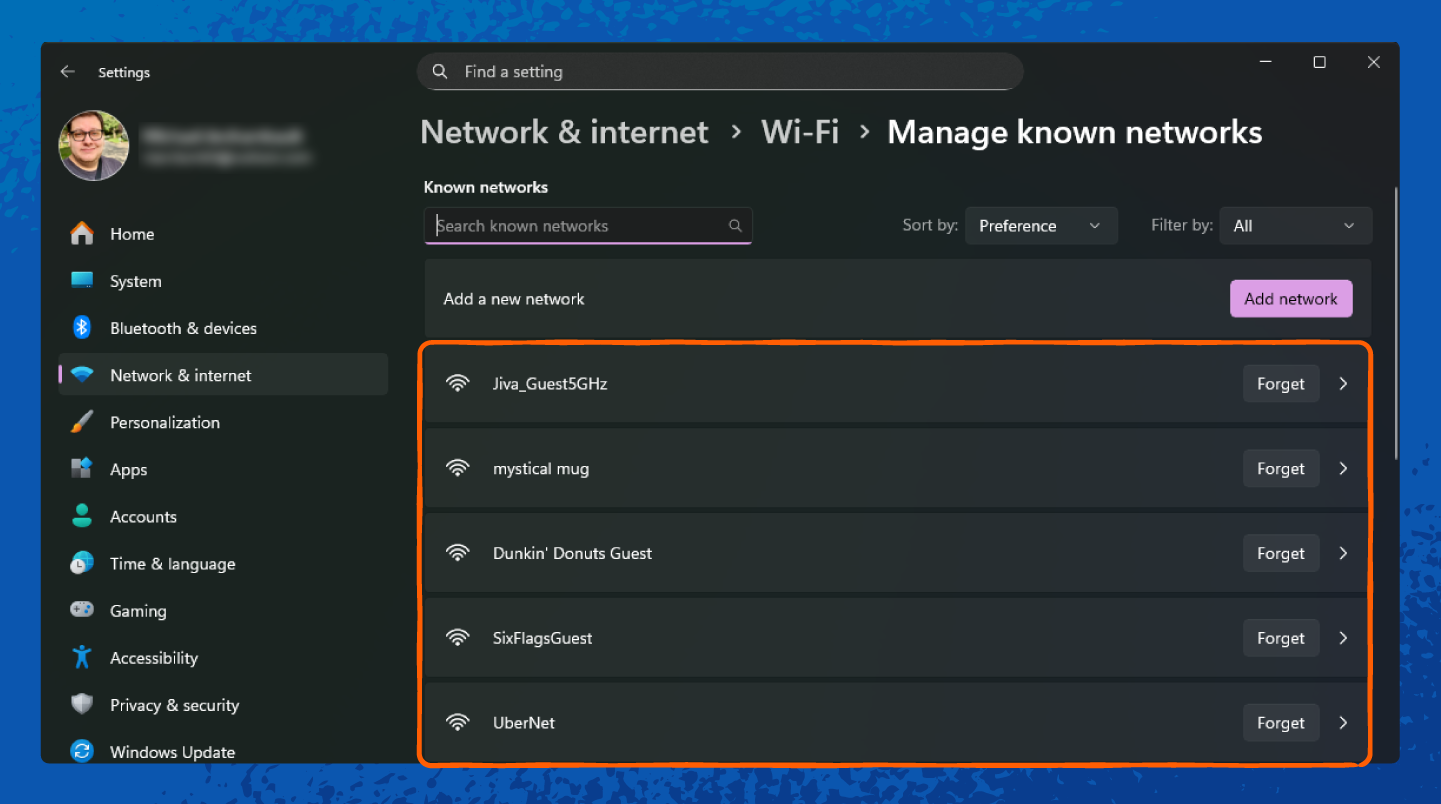
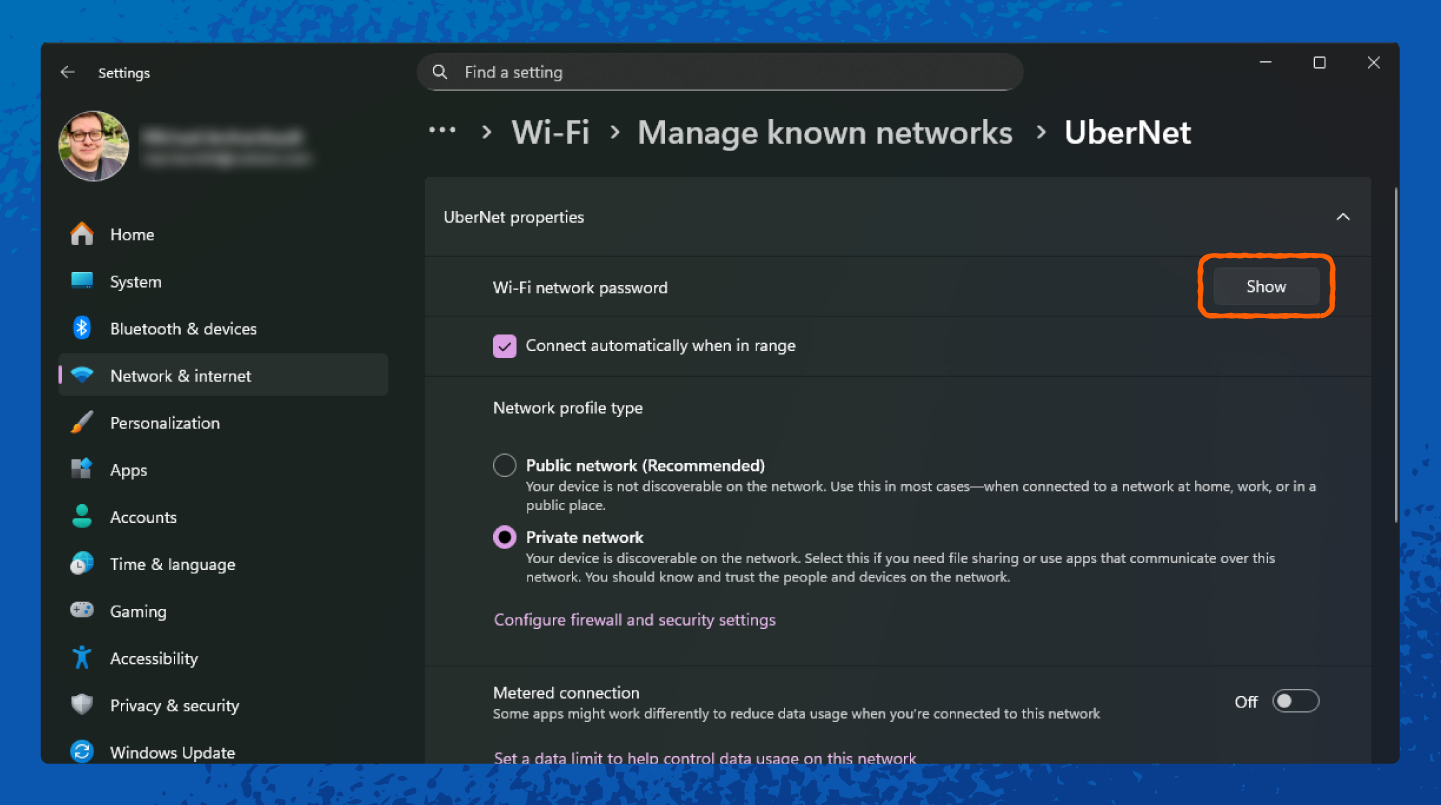
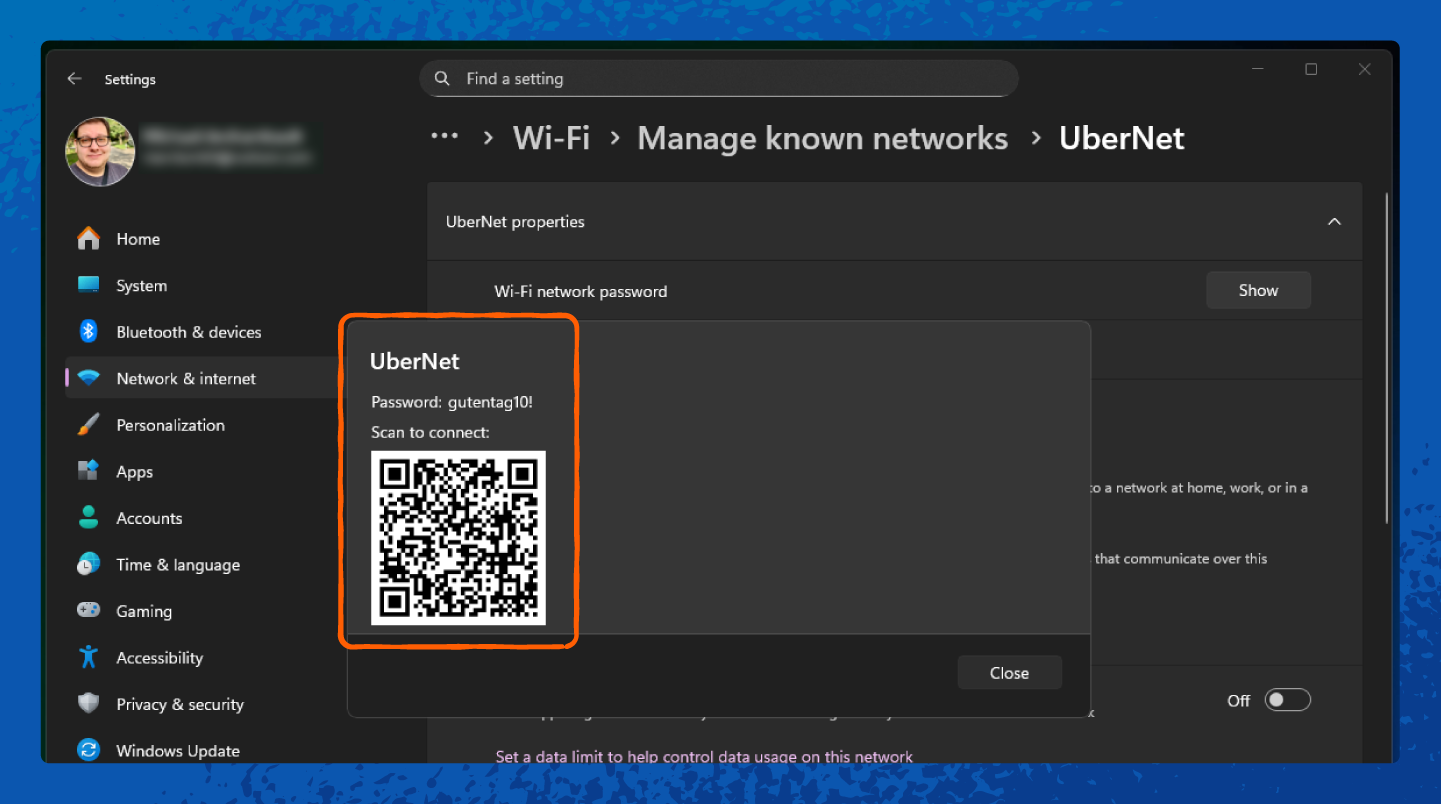
How to Find the Network Security Key on macOS
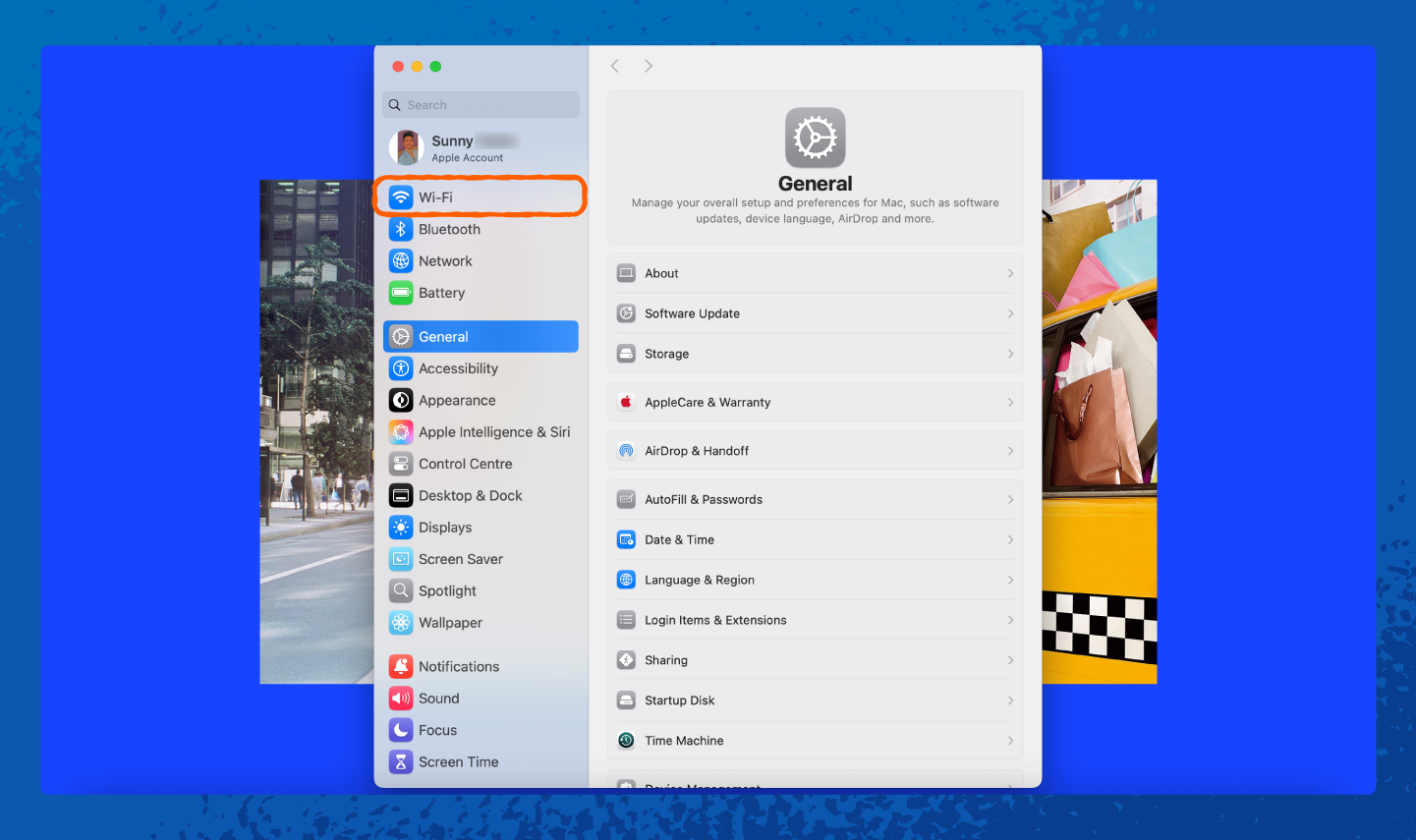
On a Mac, your saved Wi-Fi passwords are stored in the keychain, but we’ll show you an even easier way to find them:
1. Open Settings.
2. Tap on Wi-Fi.
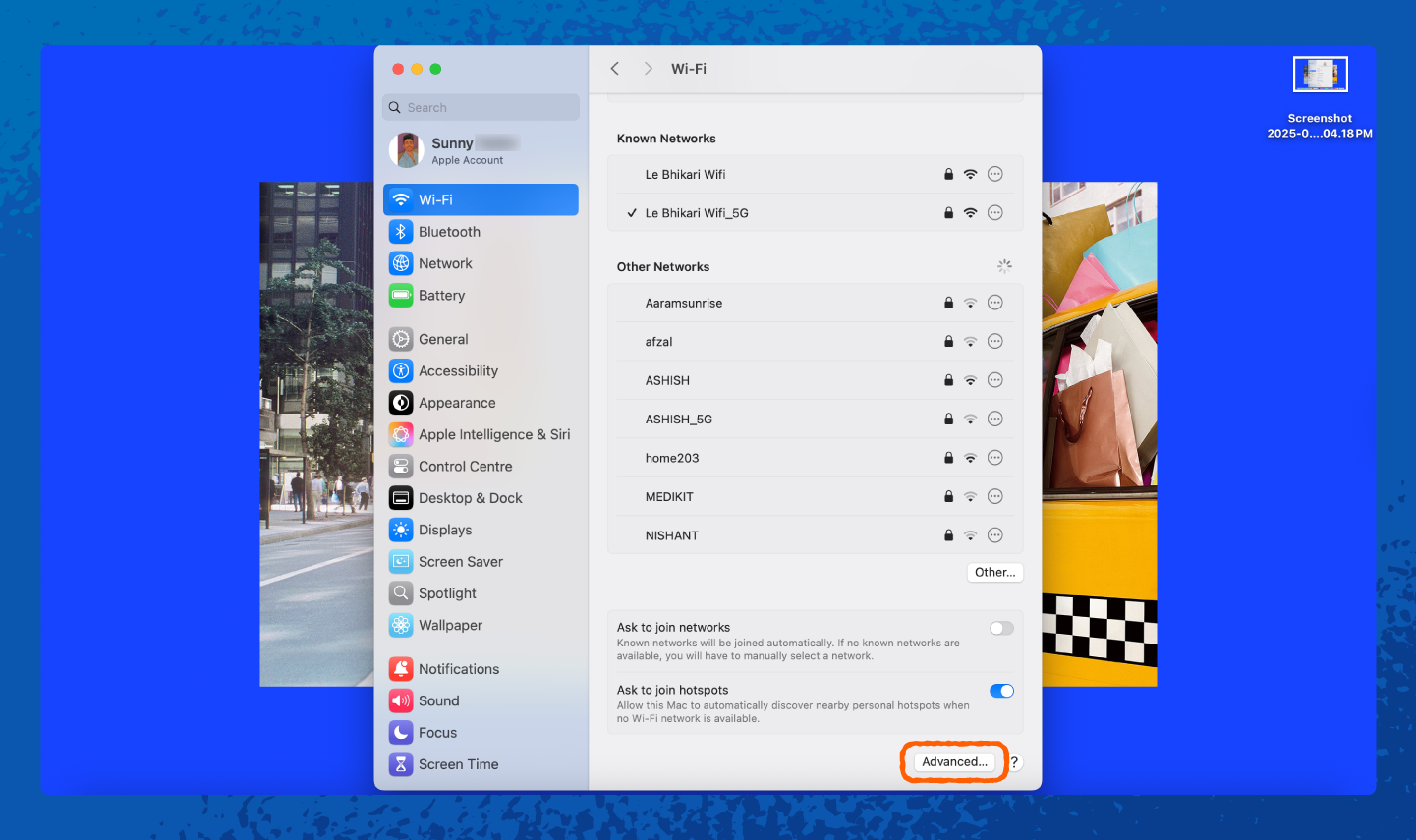
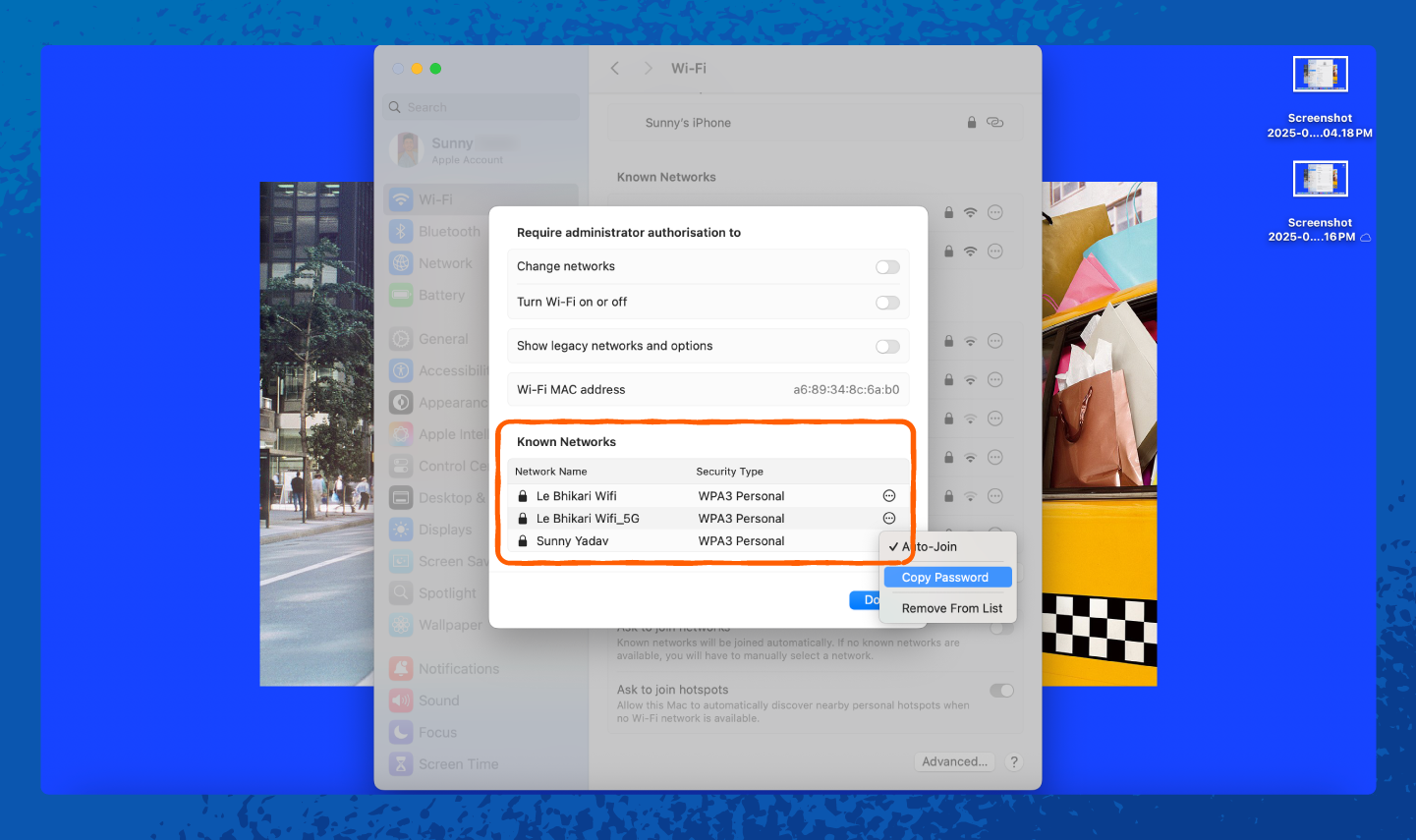
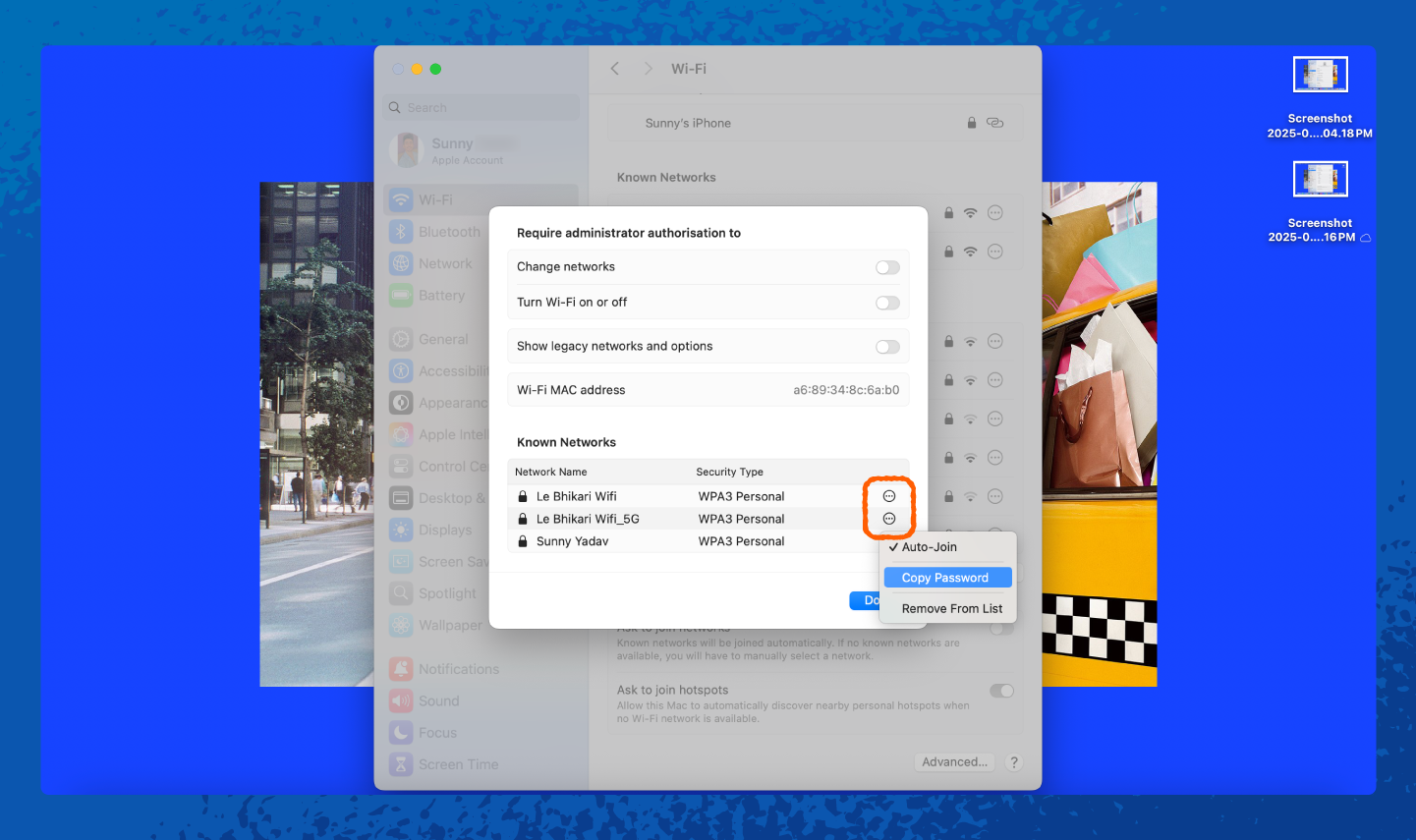
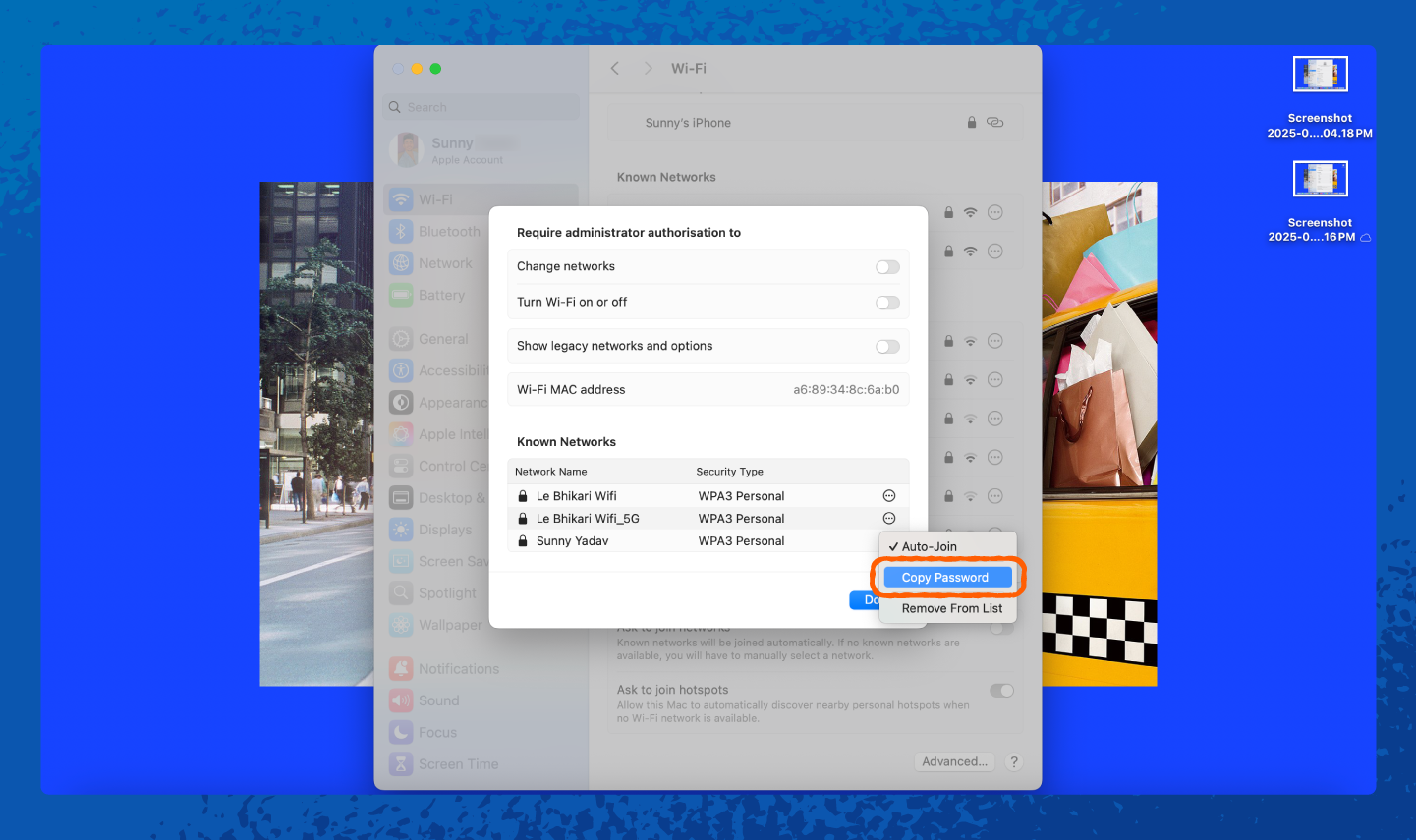
How to Change Your Network Security Key
Our password statistics found that 1 in 4 people report at least one account being compromised due to weak passwords. Changing your network security key makes it harder for outsiders to sneak onto your network.
Here’s the general way to change it through your router settings:
- Open a web browser.
- Type your router’s IP address in the address bar — common ones are 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.12.
- Log in to the router’s admin panel using your username and password — default details are often on the router label.
- Go to the Wireless Settings or Wi-Fi Settings section.
- Find the Password, Network Key or Security Key field.
- Delete the old password.
- Enter a new network security key.
- Save your changes.
- Reconnect all your devices to the Wi-Fi using the new key.
Once you change the password, all your devices will be disconnected. You’ll need to reconnect them using the new password.
What Is a Network Security Key Mismatch Error?
A network security key mismatch error means the entered Wi-Fi password doesn’t match the one saved on the device or router. Here are the most common reasons for a mismatch and how to deal with them:
- Router crashed: Restart the router by turning it off, waiting 10 seconds and turning it back on.
- Wrong password: Wi-Fi passwords are case-sensitive; double-check for typos like “O” vs. “0” or “l” vs. “1.”
- Device incompatibility: Older devices may not support WPA2 or WPA3. Switching your router to mixed mode can help.
- Saved password is outdated: Forget the network on your device and reconnect using the updated password.
- Weak signal or interference: Move closer to the router or reduce obstacles, such as walls, microwaves and other electronics.
- Router settings changed: If the network name or security settings were updated, reconnect with the new details.
How to Keep Your Network Secure
A few smart habits can go a long way in protecting your network from unwanted guests or cyberattacks. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Always change the router’s default admin password since default logins are widely known and easy to exploit.
- Use a strong Wi-Fi password with a mix of upper- and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Avoid names, birthdays or anything easy to guess.
- Don’t leave your password in plain sight. Skip the sticky note on the fridge or desk, and store it securely in a password manager instead.
- Set up a guest network to keep visitors on a separate connection so your main network stays private.
- Keep your router’s firmware updated since updates often include security fixes that block new threats.
- Disable WPS and remote management because these features can create easy backdoors for hackers.
- Turn off your router when not in use for long periods to cut down on risk and save energy.
- Use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption instead of weaker standards like WEP or WPA.
How Often Should I Change My Wi-Fi Password?
Change your Wi-Fi password every six to 12 months or immediately if you suspect someone else has access. Regularly updating the password reduces the chances of old roommates, neighbors or even hackers keeping a backdoor into your network. It also helps protect against new security threats as they emerge.
Secure Your Network With Panda Security
A strong network security key, regular password updates and smart habits go a long way, but having an extra layer of protection is always a good idea. Panda Security offers features like Wi-Fi protection, which alerts you to unsafe networks, and a robust firewall to block unauthorized access.
These tools help keep your personal information and online activity secure, so you can use your devices without worrying about hackers or intruders. Check out more features that come with Panda Dome antivirus to safeguard your network today.
Network Security Key FAQ
Still have questions about network security keys? Keep reading for answers to common questions.
Why Am I Being Asked for a Network Security Key?
Your device asks for a network security key to ensure you have permission to join the Wi-Fi. It’s a way for the router to confirm you’re an authorized user before allowing access to the network and its data.
Is a Network Security Key the Same as a Wi-Fi Password?
Yes, the network security key is just another term for your Wi-Fi password.
What Is My Hotspot Network Security Key?
Your hotspot network security key is the password you set for your phone’s hotspot. It works the same way as a Wi-Fi password, but it’s not the same. Your phone has two network security keys: one for connecting to Wi-Fi and one for using it as a hotspot.
Why Do I Need a Strong Network Security Key?
A strong network security key:
- Prevents unauthorized access to your internet connection and browsing history
- Protects sensitive data like banking info or personal messages
- Helps secure any smart home devices connected to your network
The stronger the key, the harder it is for hackers to crack it.
How Do You Crack Network Security Keys?
Hackers can use software tools to guess weak passwords or exploit old security standards like WEP. Strong, complex keys with WPA2 or WPA3 encryption make this much harder and protect your network from unauthorized access.
What Are the Differences Between WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3 Keys?
These are different security standards for Wi-Fi:
- WEP is outdated and weak.
- WPA improved security, but it is now largely outdated.
- WPA2 is widely used and strong.
- WPA3 is the newest, most secure standard with advanced encryption and protection.
How Can I Find the Network Security Key Without an Internet Connection?
If you’re offline, you can find your network security key on a sticker on your physical router. Or you can check saved Wi-Fi passwords on a device that has connected before.






