Identity theft is a prevalent issue that affects millions of people annually. You’ve certainly heard of it, but what does it entail? Identity theft is when someone steals your Social Security number, bank info and other personal details to commit criminal acts in your name.
In 2022, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received over 5 million stolen identity complaints from U.S. citizens, and with attacks getting more advanced, the chances of becoming a victim increase daily.
Although the numbers are startling, we’ve selected the 31 most concerning identity theft statistics to help you understand how to secure your identity.
How Common Is Identity Theft?
-
In 2022, the FTC received 5.1 million financial theft reports for fraud, of which 1.1 million were identity theft claims.
-
In 2022, 61% of U.S. identity theft victims had their accounts hijacked or taken over, compared to 32% with new accounts opened in their names.
-
In 2022, out of 12,911 U.S. victims, 8% suffered two identity theft incidents.
-
Credit card fraud was the number one form of identity theft in 2022, behind bank fraud and loan fraud.
-
The most common identity theft incidents of 2023 in order from most prevalent to least:
- Bank account, credit cards and check information
- Fraudulent income tax and unemployment claims
- Misuse of personal identifiable information in childhood
- Phone and utility accounts opened in the victim’s name (PII)
- Using identity to take out car, home and student loans
- Nonfinancial criminal offenses like impersonation
-
In the U.S. 80% of identity compromises in 2022 included the use of identification credentials, up from 77% from the previous year.
Cost of Identity Theft
The financial costs of identity theft are significant, ranging from stolen funds and unauthorized transactions to the expenses involved in reclaiming your identity. The statistics below uncover the financial burdens of identity theft.
-
Out of 726,000 imposter scam reports in 2022, 22% of victims lost money in the U.S., with losses totaling $2.7 billion.
-
U.S. victims of identity theft had a collective loss of $189 million in 2022, less than the combined loss of $278 million in 2021.
Stats on Personal Data Breaches
The more we rely on digital technology, the more vulnerable we are to data leaks. These leaks can lead to identity theft, as they expose personal information. Many of these leaks stem from phishing, which is a cybercrime intended to deceive people into disclosing their personal information, including credit card information and Social Security numbers. Here are identity theft statistics related to data leaks.
-
Over 10 billion personal records have been exposed globally due to data breaches since March 2020.
-
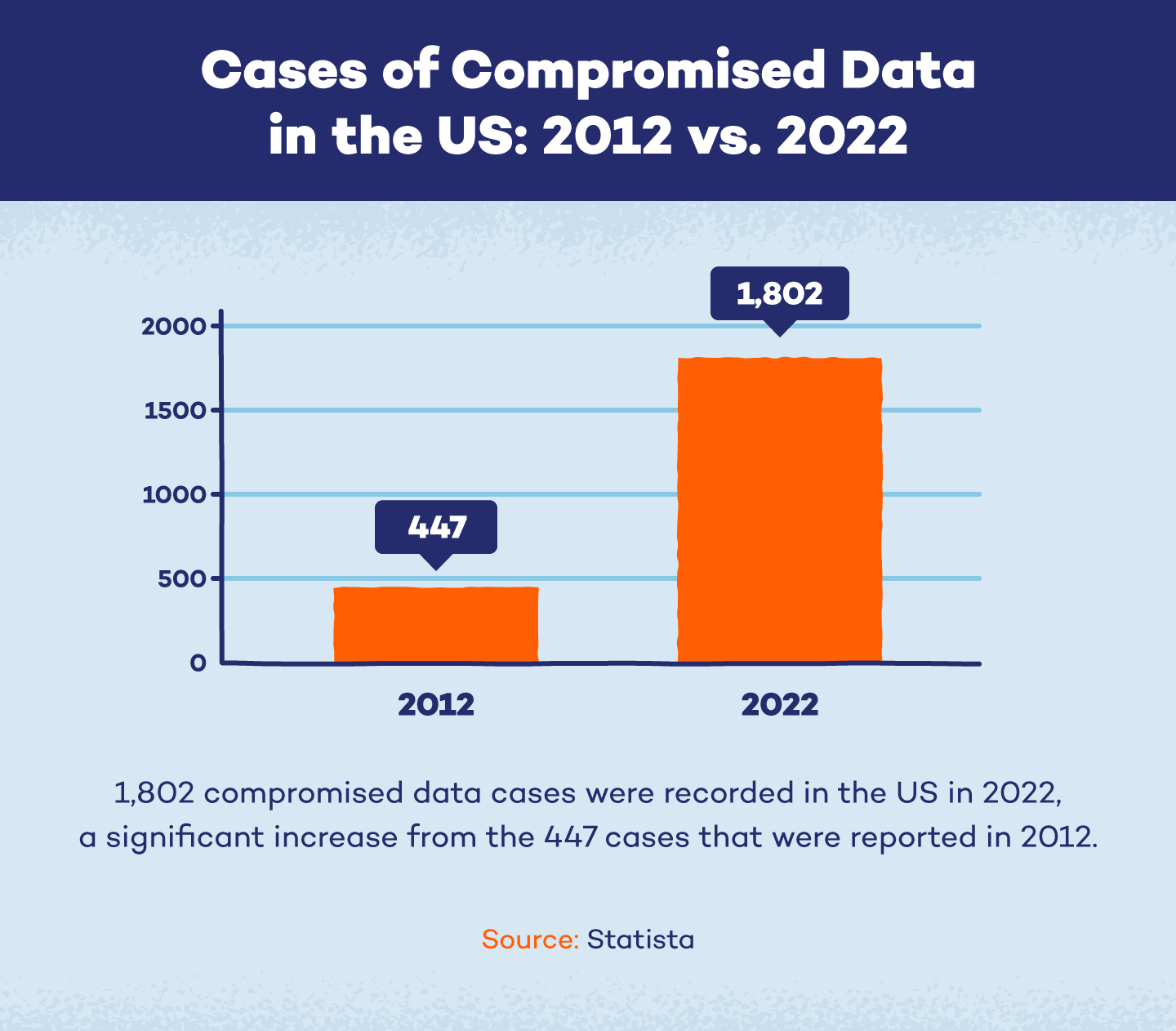
In 2022, the U.S. documented 1,802 cases of hacked data, a 300% rise from the 447 cases reported in 2012.
-
Phishing affected over 300,000 Americans in 2022.
-
There were over 1.35 million phishing sites worldwide in 2022.
-
In 2022, nearly 60,000 personal data breaches occurred in the U.S., revealing emails, passwords, payment logs and IP addresses.
-
In 2022, over 422 million U.S. people were affected by data compromises, including data breaches, leakage and exposure.
Global Identity Theft Statistics
Identity theft is a global problem and some regions lack the information or resources necessary to protect themselves or decide what to do after experiencing it. These figures demonstrate the global reach of identity theft.
-
In a 2023 global poll, 75% of Japanese adults claimed they wouldn't know how to react to identity theft, and 8 out of 10 adults in Japan and New Zealand were unsure how to check for it.
-
From 2021 to 2022 the number of cyber identity theft complaints in the U.S. decreased from 51,000 to nearly 28,000.
-
In 2023, adults who were not aware of identity theft checks were most common in countries like Australia and France (74%) and Japan and New Zealand (81%)
-
Cyber identity theft crimes increased dramatically in Europe from 566,000 reported instances in 2019 to 682,000 incidents in 2020.
-
8.6 million UK citizens (16%) have used false, fraudulent or stolen identities as of 2023.
Identity Theft Statistics By Age and Generation
This section explores identity theft trends by age and generation. Younger generations are more vulnerable due to online activity like social media fraud and potential security lapses, while criminals target senior citizens for their trust and assets (FTC). No matter your age, you can protect yourself against identity theft by being aware of typical warning signs.
-
In 2022, Gen Xers and Baby Boomers were the most likely to report incidents of identity theft (both at 81%), compared to Gen Zers and Millennials, who reported 59% and 69% of cases, respectively.
-
In 2022, Gen Z adults living in the U.S., U.K. and Canada topped the list for falling victim to phishing scams, with 34% admitting they've been tricked by hackers into revealing their information.
-
Compared to 16% (8.6 million) of the total population, 33% (2 million) of youths in the United Kingdom (16-24) used a false or stolen identity to get credit, products or services in 2023.
-
U.S., U.K. and Canada-based millennials experienced higher rates of identity theft (20%) than any other age group in 2022.
-
In 2022, the second most targeted age group in the U.S. for identity theft is 40- to 49-year-olds.
-
In 2022, Gen Zers (18%) had the second highest reported victimization rates for identity theft.
-
In 2022, the most targeted age group in the U.S. for identity theft is 30- to 39-year-olds.
States with the Highest Identity Theft Rates
Where you live in the United States affects how vulnerable you are to identity theft due to various factors like income, crime rates and more. Although it can happen anywhere in the world, living in these states increases your risk of identity theft.

Identity Theft Preventive Measures
You can prevent identity theft with the proper knowledge and safety measures. A 2022 cybersecurity survey found that 45% of people who were educated about identity theft prevention used stronger passwords, 40% updated security, using multi-factor authentication and 58% were better at spotting phishing messages.
To protect yourself from identity theft, here’s what we recommend.
- Create stronger passwords: Use a mix of letters, numbers and symbols to create a solid password. Use longer phrases instead of single words, like Mary3hadalittleL@mb! and avoid using your name or the same password for multiple accounts.
- Check bank statements and credit reports: Regularly review your bank statements for unauthorized transactions and check your credit report for fraud. You can obtain a free report from Annualcreditreport.com.
- Use MFA or 2FA: Implementing multi-factor or two-factor authentication adds a layer of security by requiring a second step, like an email or text code, to authorize your account.
- Utilize cybersecurity software: Secure your electronic devices with antivirus and security software. These updates make it harder for hackers to infiltrate your systems.
- Protect your Social Security number: Hackers can damage your name and Social Security number, so limit giving it out unless necessary.
- Limit sharing on social platforms: Limit social media sharing, especially if you use the data for passwords or security questions, as criminals can exploit this information.
- Secure your network: Avoid accessing sensitive data on public Wi-Fi networks. Use private browsers, VPNs and privacy-focused search engines to help prevent identity theft.
What to Do If Your Identity Is Stolen
If your identity is stolen, report it to the FTC right away. Delayed reporting will only make matters worse for your finances. The proper institutions can freeze your accounts and possibly remove fraudulent accounts in your name. There are three ways to report identity theft:
- Report to the FTC at Identitytheft.org.
- Alert the three credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax and Transunion).
- Call the fraud department at your banking institution.
Stay Protected With Panda Security
As technology advances, so do malicious tactics like phishing, making our data more vulnerable to theft. As you can see from these statistics, it impacts millions of people each year, and anyone can be a victim.
The most important thing you can do to avoid becoming a victim is prioritize your online security. Implement safeguards like our Panda Security Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet connection, keep a close eye on your financial records and develop sound cybersecurity habits. Although identity theft is a real problem, you can stay safe if you take the proper steps.




















1 comment
I recently had a word with an “IT guy” who told me that the best password doesn’t have to be complicated. He claimed it should be long, however, it is supposed to be easier to crack the random characters instead of the simple ones (I’m particularly referring to numbers). Do you have any thoughts about that? Assuming they both have the same length – which one is better: “1749…” or”1111…”?