Staying informed about the latest trends in cybersecurity is crucial in today’s increasingly digital world. Being in the know isn’t just for information technology (IT) professionals, either; it’s essential knowledge for anyone who uses a computer, smartphone or smart device. As cyber threats become more sophisticated with the power of artificial intelligence (AI), understanding these trends can help protect you against hackers.
We surveyed 258 cybersecurity professionals to identify the most critical data security trends of 2025 that everyday users should be aware of. From the rising threat of AI-powered attacks to the best defense for your home devices, here’s what the experts want you to know.
Key Takeaways
- Over 82.6% of cybersecurity professionals are very or moderately concerned about the increasing sophistication of AI-powered phishing attacks.
- 87.6% of cybersecurity experts believe that AI-powered threat detection will decrease the volume of successful cyberattacks.
- The vast majority of cybersecurity professionals (over 98%) currently follow a Zero Trust model.
- A substantial percentage (42.6%) of cybersecurity professionals identify inadequate employee security awareness as a key challenge of remote/hybrid work.
- Over a quarter of experts consider multi-factor authentication (MFA) the single most important security measure for everyday users.
1. Cybersecurity Professionals Are in an AI Arms Race With Hackers
We’ve entered a new era of cybersecurity as both defenders and attackers are leveraging artificial intelligence, creating what experts describe as an “AI arms race” in the cybersecurity world.
Our survey revealed that an overwhelming 82.6% of cybersecurity professionals are either “very concerned” (50.4%) or “moderately concerned” (32.2%) about the increasing sophistication of AI-powered phishing attacks.
This concern stems from hackers weaponizing artificial intelligence to create more convincing and targeted attacks. Historically, phishing emails have been relatively easy to spot due to poor grammar or generic greetings, but AI can now generate highly personalized messages that mimic the writing style of trusted contacts or organizations.
When asked about the trending threats they’re most worried about in 2025, cybersecurity professionals highlighted:
- AI-driven malware (43.4%)
- AI-enhanced password cracking (39.2%)
- Ransomware as a service (38.4%)
- Supply chain attacks (32.6%)
- Shadow IT (33.6%)
- IoT device vulnerabilities (30.2%)
- Deepfakes (27.5%)
- Fileless malware attacks (24.8%)
- Quantum computing (20.9%)
- Third-party vendors (19.77%)
- 5G (17.4%)
It’s notable that some much-discussed cybersecurity trends, such as the perceived threat of 5G, registered as a lower concern among professionals compared to the other clear and present dangers like AI-powered malware, suggesting a divergence between public perception and expert priorities in the threat landscape.
The good news is that cybersecurity professionals aren’t standing still; they’re also harnessing the power of AI to develop more sophisticated defenses.

2. Experts See a Bright Future in AI-Powered Cyber Defense
Despite concerns about AI-powered attacks, future trends in cybersecurity show that professionals remain optimistic about using AI as a defensive tool. A remarkable 87.6% of professionals believe that AI-powered threat detection will decrease the volume of successful cyberattacks:
- 38% expect a 40%-60% decrease
- 23.3% predict a 60%-80% decrease
- 21.3% anticipate a 20%-40% decrease
- 5.8% believe we’ll see an 80%-100% decrease
This optimism likely stems from AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate an attack, often faster and more accurately than human analysts. AI-powered security systems can continuously monitor networks, automatically respond to threats and learn from new attack methods to improve their detection capabilities.
It’s worth noting that not all professionals share this optimism: 5% think AI-powered threat detection won’t affect the volume of successful attacks, while 6.6% believe it might actually increase successful attacks. This minority view reminds us that technology alone isn’t a silver bullet — proper implementation and human oversight remain essential.
3. Your Smart Devices Could Be an Open Door for Hackers, Warn Nearly 90% of Cybersecurity Pros
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in our homes, from smart speakers and thermostats to connected refrigerators and doorbell cameras, has created new entry points for cybercriminals. An overwhelming 87.2% of cybersecurity professionals expressed concern about security vulnerabilities associated with IoT devices in homes, with 46.5% being “very concerned” and 40.7% “moderately concerned.”
These smart devices often lack robust security features for several reasons:
- Many prioritize convenience and ease of setup over security.
- Some users use default or weak passwords and don’t change them.
- Many devices receive infrequent security updates.
- IoT manufacturers may have limited security expertise compared to established tech companies.
A compromised smart device can serve as a gateway to your entire home network, potentially exposing personal data, enabling surveillance or even becoming part of a botnet used in larger attacks. As the average home accumulates more connected devices, this vulnerability becomes alarmingly significant in network security trends.
4. AI Phishing Poses a Threat to Even the Most Confident Cybersecurity Pros

Despite 94% of cybersecurity professionals reporting they feel “very confident” (50.8%) or “moderately confident” (43.8%) in their organization’s current methods for protecting user data, many of these same professionals express significant concern about AI-powered phishing attacks. This highlights an important reality: Even the best-protected organizations recognize the looming threat of AI on cybersecurity.
The reason for this concern is clear — AI-powered phishing represents a massive technological advancement for scammers. These attacks can:
- Analyze social media profiles to craft highly personalized messages
- Create believable messages from a trusted contact
- Generate convincing fake websites that appear identical to legitimate ones
- Time attacks based on a victim’s online activity patterns
- Scale these personalized attacks to thousands of targets simultaneously
Trying to spot threats on your own is risky if you’re not accustomed to the advancements in phishing technology. Even cybersecurity professionals with years of experience are concerned about these new tactics, which should serve as a wake-up call for families and home users.
5. Ransomware Is a Top Threat for Organizations
When asked about the most frequently encountered cybersecurity threats beyond phishing and viruses, ransomware emerged as the top concern, with 21.7% of professionals identifying it as the threat their organization faces most often. This was followed by DDoS attacks at 19.8%, a finding that aligns with broader IT security trends showing ransomware’s persistent threat.
Ransomware attacks are when hackers encrypt an organization’s data and demand payment for its release. These attacks on businesses aren’t just abstract corporate problems; they directly affect consumers as well.
You may be affected by ransomware attacks when hackers:
- Threaten your health care provider with releasing patient records
- Hack a bank, making their services temporarily unavailable
- Attempt to expose your personal information from a retailer
- Disrupt essential services like utilities or transportation
Data from Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report confirms that ransomware is becoming a major issue in a wide range of industries. It found that ransomware was a top threat across 92% of industries, with 32% of all breaches involving ransomware or extortion.
6. Remote Work Arrangements Open the Door to Unique Cyber Threats
The rapid shift to remote and hybrid work models has introduced distinct cybersecurity challenges. While increased phishing attacks have emerged as a primary concern for organizations with remote workers, cited by 52.7% of professionals, it’s not the only area of heightened risk.
Our survey also revealed significant worries about threats stemming from within organizations, with 39.9% identifying increased insider threats as a top challenge in remote settings. Furthermore, 42.6% of cybersecurity professionals highlighted inadequate employee security awareness as a major concern in these flexible work arrangements.
Beyond these top concerns, cybersecurity professionals also identified other significant challenges associated with remote and hybrid work, including:
- Secure access to cloud resources (45.7%)
- Inadequate employee security awareness (42.6%)
- Compromised home (39.9%)
- Increased insider threats (39.9%)
- Lack of visibility into remote user activity (38.8%)
- Data exfiltration from personal devices (36.8%)
- Difficulty patching remote devices (31%)
Remote workers face a confluence of vulnerabilities due to:
- Outside corporate protections: Operating without the traditional security measures of a corporate network
- Personal device use: Increased risk due to potential lack of robust security on personal devices
- Limited IT support: Less direct access to on-site IT assistance for immediate security issues
- Phishing targets: More susceptible to sophisticated phishing attempts in less controlled environments
- Blurred work-life lines: Increased chance of unintentional data mishandling due to overlap
- Reduced oversight: Greater opportunities for both malicious and accidental insider threats due to less monitoring
This vulnerability, combined with the rise of AI-powered phishing, creates a perfect storm of risk. Cybersecurity professionals recommend that remote workers protect themselves and their organizations by implementing security measures like MFA, regular software updates and comprehensive antivirus protection.

7. The Technology Sector Is at the Highest Risk of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity professionals identified the technology sector as facing the biggest cybersecurity threats, with 69.8% selecting it among the top three most vulnerable industries. This was followed by:
- Financial services (64%)
- Government/public sector (38%)
- Health care (36%)
- Energy/utilities (27.9%)
- Manufacturing/industrial IoT (27.1%)
- Retail/e-commerce (26.7%)
The irony isn’t lost on experts — the very industry that should be most familiar with cyber threats appears to be the most targeted. Several factors contribute to this vulnerability:
- Their systems are frequently connected to partner networks, creating multiple entry points.
- The industry’s rapid pace can sometimes prioritize innovation over security.
- Tech companies often possess valuable intellectual property.
- They maintain extensive user data that’s attractive to attackers.
For the average user, this means that even services from tech giants require careful attention to security. It’s important not to assume that a company’s technical sophistication automatically translates to bulletproof security for personal information.
8. A Zero Trust Model Is Now a Cybersecurity Expectation
The concept of “Zero Trust,” or operating under the assumption that no user or device should be trusted by default, even those inside the network perimeter, has become standard practice. A notable 98.1% of professionals report their organizations now follow a Zero Trust model, with 86% finding it either “very effective” (43.4%) or “moderately effective” (43%) at reducing cyber threats.
The shift to Zero Trust means that everyday users will likely encounter more frequent authentication requirements and limited access to resources based on specific roles and needs. While these are minor inconveniences, they significantly enhance security.
9. Multi-Factor Authentication Is Your Best Defense Against Hackers
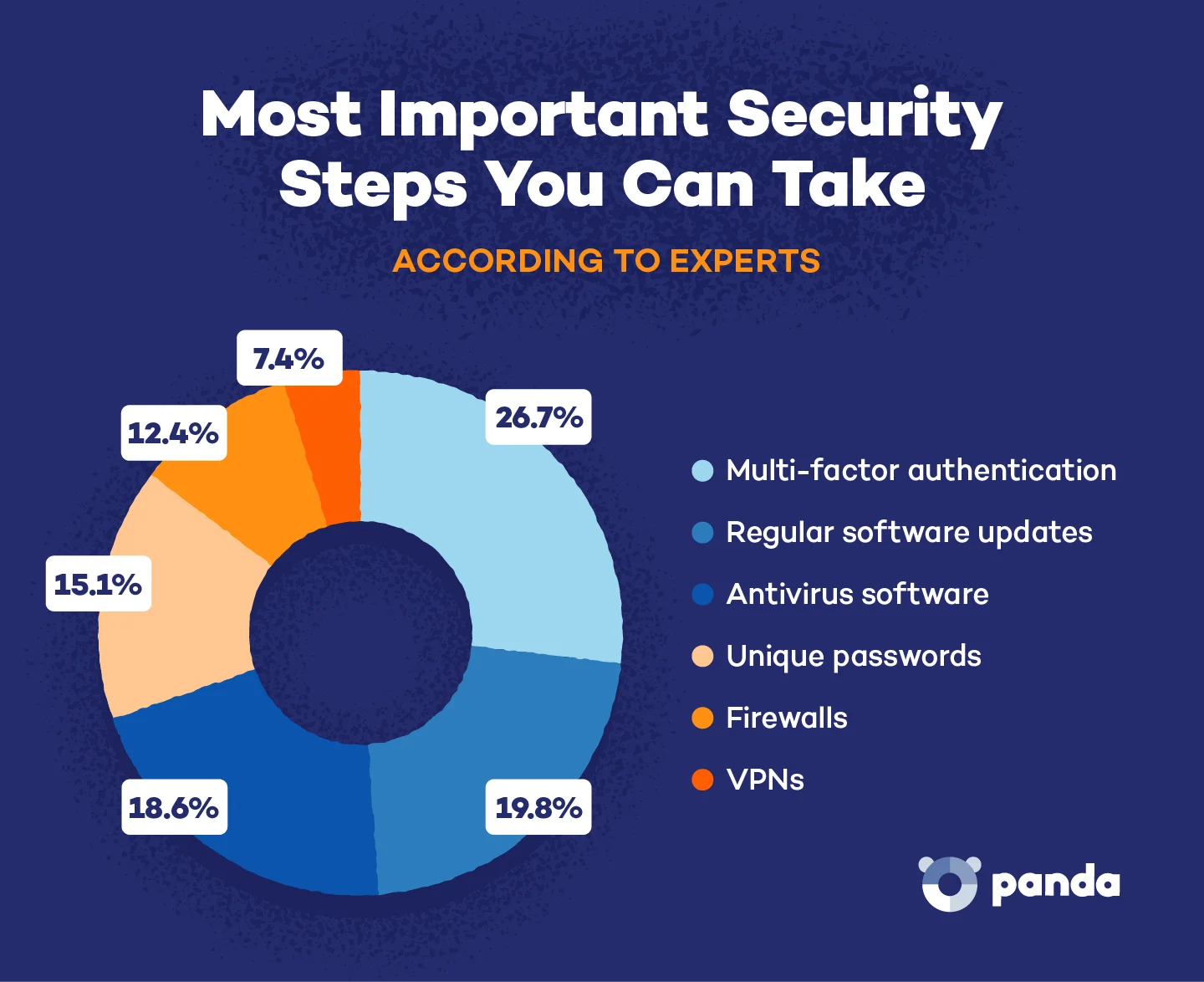
When we asked cybersecurity professionals about the single most important security measure everyday users should implement, the answer was clear. Multi-factor authentication topped the list at 26.7%, making it the #1 recommendation from security experts for protecting your digital life.
Think of MFA as adding extra locks to your digital doors. Instead of just needing a password, you’ll also need a second verification factor, like a code sent to your phone or email. This makes it significantly harder for hackers to break into your accounts, even if they manage to steal your password.
Other important security measures experts recommend include:
- Regular software updates (19.8%)
- Antivirus software (18.6%)
- Strong, unique passwords with 12+ mixed characters (15.1%)
- Firewalls (12.4%)
- VPNs (7.4%)
While each of these measures plays a crucial role in your overall security posture, MFA provides that critical second layer of defense against unauthorized access. By implementing MFA on your most important accounts, like email, banking and social media, you create a much stronger barrier against cybercriminals.
Stay Ahead of Cyber Threats With Panda Security
The cybersecurity industry trends we’ve explored highlight the ever-evolving threats we face in our increasingly digital world. From sophisticated AI-powered phishing to vulnerabilities in our connected devices, staying informed and proactive is key to safeguarding your online life. As hackers become more advanced, implementing strong security practices is a must.
Panda Security offers a powerful suite of features designed to help you stay protected against these very threats. Panda Dome includes real-time protection against malware and viruses, advanced anti-phishing technology and protection for your connected home devices. Don’t leave your digital security to chance — try Panda Dome today.
Methodology
The survey of 258 U.S. cybersecurity professionals was conducted via Centiment Audience for Panda Security between March 24 and March 26, 2025. Data is unweighted and the margin of error is approximately +/-3% for the overall sample with a 95% confidence level.





